Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Beneficial Effects of Flavonoids for Neuroprotection
- PMID: 34071978
- PMCID: PMC8199014
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115719
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling in the Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease: Beneficial Effects of Flavonoids for Neuroprotection
Abstract
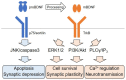
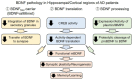
The function of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) via activation through its high-affinity receptor Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) has a pivotal role in cell differentiation, cell survival, synaptic plasticity, and both embryonic and adult neurogenesis in central nervous system neurons. A number of studies have demonstrated the possible involvement of altered expression and action of the BDNF/TrkB signaling in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD). In this review, we introduce an essential role of the BDNF and its downstream signaling in neural function. We also review the current evidence on the deregulated the BDNF signaling in the pathophysiology of AD at gene, mRNA, and protein levels. Further, we discuss a potential usefulness of small compounds, including flavonoids, which can stimulate BDNF-related signaling as a BDNF-targeting therapy.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; flavonoids; intracellular signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor as an Essential Mediator in Neuronal Functions and the Therapeutic Potential of Its Mimetics for Neuroprotection in Neurologic and Psychiatric Disorders.Molecules. 2025 Feb 12;30(4):848. doi: 10.3390/molecules30040848. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40005159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking Alzheimer's Disease: The Role of BDNF Signaling in Neuropathology and Treatment.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 May 17;27(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s12017-025-08857-x. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40380033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of BDNF Signaling in the Neuroprotective and Memory-enhancing Effects of Flavonoids in Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024;23(8):984-995. doi: 10.2174/1871527323666230912090856. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37702162 Review.
-
Blocking GSK3β-mediated dynamin1 phosphorylation enhances BDNF-dependent TrkB endocytosis and the protective effects of BDNF in neuronal and mouse models of Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Feb;74:377-91. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.11.020. Epub 2014 Dec 5. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 25484286
-
Roles of brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase B (BDNF/TrkB) signalling in Alzheimer's disease.J Clin Neurosci. 2012 Jul;19(7):946-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2011.12.022. Epub 2012 May 20. J Clin Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22613489 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain region-specific roles of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in social stress-induced depressive-like behavior.Neural Regen Res. 2025 Jan 1;20(1):159-173. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-23-01419. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Neural Regen Res. 2025. PMID: 38767484 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease is an inherent, natural part of human brain aging: an integrated perspective.Free Neuropathol. 2022 Jul 8;3:17. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2022-3806. eCollection 2022 Jan. Free Neuropathol. 2022. PMID: 37284149 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Membrane-Derived Nanoparticles for Isoliquiritin Enhanced Glioma Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;15(9):1059. doi: 10.3390/ph15091059. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145280 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress Plays an Important Role in Glutamatergic Excitotoxicity-Induced Cochlear Synaptopathy: Implication for Therapeutic Molecules Screening.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jan 25;13(2):149. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020149. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397748 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Microglia in the Development of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 12;9(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101449. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680566 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Numakawa T., Odaka H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurogenesis. In: Martin C., Preedy V., Rajendram R., editors. Factors Affecting Neurodevelopment: Genetics, Neurology, Behavior, and Diet. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021.
-
- Moreno-Jiménez E.P., Flor-García M., Terreros-Roncal J., Rábano A., Cafini F., Pallas-Bazarra N., Ávila J., Llorens-Martín M. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is abundant in neurologically healthy subjects and drops sharply in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019;25:554–560. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0375-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hock C., Heese K., Hulette C., Rosenberg C., Otten U. Region-specific neurotrophin imbalances in Alzheimer disease: Decreased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and increased levels of nerve growth factor in hippocampus and cortical areas. Arch. Neurol. 2000;57:846–851. doi: 10.1001/archneur.57.6.846. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

