Pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) By-Products Valorization: Novel Bio Ingredients for Functional Foods
- PMID: 34072026
- PMCID: PMC8198275
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26113216
Pineapple (Ananas comosus L.) By-Products Valorization: Novel Bio Ingredients for Functional Foods
Abstract
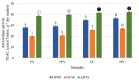
Pineapple is consumed on a large scale around the world due to its appreciated sensorial characteristics. The industry of minimally processed pineapple produces enormous quantities of by-products (30-50%) which are generally undervalued. The end-of-life of pineapple by-products (PBP) can be replaced by reuse and renewal flows in an integrated process to promote economic growth by reducing consumption of natural resources and diminishing food waste. In our study, pineapple shell (PS) and pineapple core (PC), vacuum-packed separately, were subjected to moderate hydrostatic pressure (225 MPa, 8.5 min) (MHP) as abiotic stress to increase bromelain activity and antioxidant capacity. Pressurized and raw PBP were lyophilized to produce a stable powder. The dehydrated samples were characterized by the following methodologies: chemical and physical characterization, total phenolic compounds (TPC), antioxidant capacity, bromelain activity, microbiology, and mycotoxins. Results demonstrated that PBP are naturally rich in carbohydrates (66-88%), insoluble (16-28%) and soluble (2-4%) fiber, and minerals (4-5%). MHP was demonstrated to be beneficial in improving TPC (2-4%), antioxidant activity (2-6%), and bromelain activity (6-32%) without affecting the nutritional value. Furthermore, microbial and mycotoxical analysis demonstrated that powdered PC is a safe by-product. PS application is possible but requires previous decontamination to reduce the microbiological load.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; novel food ingredient; pineapple by-products; sustainability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Antoniolli L.R., Benedetti B.C., Souza Filho M.S.M., Borges M.F. Avaliação da vanilina como agente antimicrobiano em abacaxi “Pérola” minimamente processado. Ciênc. Tecnol. Aliment. 2004;24:473–477. doi: 10.1590/S0101-20612004000300029. - DOI
-
- Hossain M.A., Rahman S.M.M. Total phenolics, flavonoids and antioxidant activity of tropical fruit pineapple. Food Res. Int. 2011;44:672–676. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.11.036. - DOI
-
- Hossain M.F. Nutritional Value and Medicinal Benefits of Pineapple. Int. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2015;4:84. doi: 10.11648/j.ijnfs.20150401.22. - DOI
-
- Debnath P., Dey P., Chanda A., Bhakta T. A Survey on Pineapple and its medicinal value. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2012;1:24–29.
-
- Corzo C.A., Waliszewski K.N., Welti-Chanes J. Pineapple fruit bromelain affinity to different protein substrates. Food Chem. 2012;133:631–635. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.05.119. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

