Biplanar High-Speed Fluoroscopy of Pony Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon (SDFT)-An In Vivo Pilot Study
- PMID: 34072030
- PMCID: PMC8228745
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci8060092
Biplanar High-Speed Fluoroscopy of Pony Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon (SDFT)-An In Vivo Pilot Study
Abstract
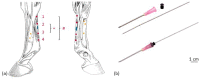
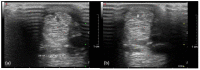
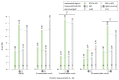
The superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT) is the most frequently injured structure of the musculoskeletal system in sport horses and a common cause for early retirement. This project's aim was to visualize and measure the strain of the sound, injured, and healing SDFTs in a pony during walk and trot. For this purpose, biplanar high-speed fluoroscopic kinematography (FluoKin), as a high precision X-ray movement analysis tool, was used for the first time in vivo with equine tendons. The strain in the metacarpal region of the sound SDFT was 2.86% during walk and 6.78% during trot. When injured, the strain increased to 3.38% during walk and decreased to 5.96% during trot. The baseline strain in the mid-metacarpal region was 3.13% during walk and 6.06% during trot and, when injured, decreased to 2.98% and increased to 7.61%, respectively. Following tendon injury, the mid-metacarpal region contributed less to the overall strain during walk but showed increased contribution during trot. Using this marker-based FluoKin technique, direct, high-precision, and long-term strain measurements in the same individual are possible. We conclude that FluoKin is a powerful tool for gaining deeper insight into equine tendon biomechanics.
Keywords: XROMM; collagenase; equine; gait; horse; strain; tendinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Smith R.K.W., Birch H.L., Goodman S., Heinegård D., Goodship A.E. The influence of ageing and exercise on tendon growth and degeneration–Hypotheses for the initiation and prevention of strain-induced tendinopathies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2002;133:1039–1050. doi: 10.1016/S1095-6433(02)00148-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wollenman P., McMahon P.J., Knapp S., Ross M.W. Lameness in the Polo Pony. In: Ross M.W., Dyson S.J., editors. Diagnosis and Management of Lameness in the Horse. 2nd ed. Elsevier/Saunders; St. Louis, MO, USA: 2011. pp. 1149–1164.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

