Mechanisms of Immune Escape and Resistance to Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapies in Mismatch Repair Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancers
- PMID: 34072037
- PMCID: PMC8199207
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112638
Mechanisms of Immune Escape and Resistance to Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapies in Mismatch Repair Deficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancers
Abstract
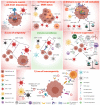
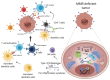
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) represent an effective therapeutic strategy for several different types of solid tumors and are remarkably effective in mismatch repair deficient (MMRd) tumors, including colorectal cancer (CRC). The prevalent view is that the elevated and dynamic neoantigen burden associated with the mutator phenotype of MMRd fosters enhanced immune surveillance of these cancers. In addition, recent findings suggest that MMRd tumors have increased cytosolic DNA, which triggers the cGAS STING pathway, leading to interferon-mediated immune response. Unfortunately, approximately 30% of MMRd CRC exhibit primary resistance to CPIs, while a substantial fraction of tumors acquires resistance after an initial benefit. Profiling of clinical samples and preclinical studies suggests that alterations in the Wnt and the JAK-STAT signaling pathways are associated with refractoriness to CPIs. Intriguingly, mutations in the antigen presentation machinery, such as loss of MHC or Beta-2 microglobulin (B2M), are implicated in initial immune evasion but do not impair response to CPIs. In this review, we outline how understanding the mechanistic basis of immune evasion and CPI resistance in MMRd CRC provides the rationale for innovative strategies to increase the subset of patients benefiting from CPIs.
Keywords: MSI; colorectal cancer; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune escape; immune evasion; immune surveillance; microsatellite instability; mismatch repair deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B. and G.G. are cofounders and shareholders of NeoPhore limited. A.B. is a member of the NeoPhore scientific advisory board. A.S.-B. is an advisory board member for Amgen, Bayer, Sanofi, Servier, and MSD. S.S. is an advisory board member for Amgen, Bayer, BMS, CheckmAb, Clovis, Daiichi-Sankyo, Merck, Roche-Genentech, and Seattle Genetics.
Figures
References
-
- Planchard D., Popat S., Kerr K., Novello S., Smit E.F., Faivre-Finn C., Mok T.S., Reck M., Van Schil P.E., Hellmann M.D., et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:iv192–iv237. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy275. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baas P., Scherpereel A., Nowak A.K., Fujimoto N., Peters S., Tsao A.S., Mansfield A.S., Popat S., Jahan T., Antonia S., et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab in unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (CheckMate 743): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2021;397:375–386. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32714-8. - DOI - PubMed

