Protective Effects of Thymoquinone, an Active Compound of Nigella sativa, on Rats with Benzo(a)pyrene-Induced Lung Injury through Regulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
- PMID: 34072086
- PMCID: PMC8199466
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26113218
Protective Effects of Thymoquinone, an Active Compound of Nigella sativa, on Rats with Benzo(a)pyrene-Induced Lung Injury through Regulation of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
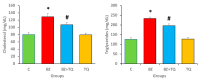
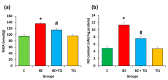
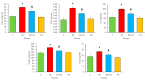
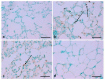
Benzopyrene [B(a)P] is a well-recognized environmental carcinogen, which promotes oxidative stress, inflammation, and other metabolic complications. In the current study, the therapeutic effects of thymoquinone (TQ) against B(a)P-induced lung injury in experimental rats were examined. B(a)P used at 50 mg/kg b.w. induced lung injury that was investigated via the evaluation of lipid profile, inflammatory markers, nitric oxide (NO), and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. B(a)P also led to a decrease in superoxide dismutase (SOD) (34.3 vs. 58.5 U/mg protein), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) (42.4 vs. 72.8 U/mg protein), catalase (CAT) (21.2 vs. 30.5 U/mg protein), and total antioxidant capacity compared to normal animals. Treatment with TQ, used at 50 mg/kg b.w., led to a significant reduction in triglycerides (TG) (196.2 vs. 233.7 mg/dL), total cholesterol (TC) (107.2 vs. 129.3 mg/dL), and inflammatory markers and increased the antioxidant enzyme level in comparison with the group that was administered B(a)P only (p < 0.05). B(a)P administration led to the thickening of lung epithelium, increased inflammatory cell infiltration, damaged lung tissue architecture, and led to accumulation of collagen fibres as studied through haematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Sirius red, and Masson's trichrome staining. Moreover, the recognition of apoptotic nuclei and expression pattern of NF-κB were evaluated through the TUNEL assay and immunohistochemistry, respectively. The histopathological changes were found to be considerably low in the TQ-treated animal group. The TUNEL-positive cells increased significantly in the B(a)P-induced group, whereas the TQ-treated group showed a decreased apoptosis rate. Significantly high cytoplasmic expression of NF-κB in the B(a)P-induced group was seen, and this expression was prominently reduced in the TQ-treated group. Our results suggest that TQ can be used in the protection against benzopyrene-caused lung injury.
Keywords: TUNEL assay; antioxidant status; benzopyrene; immunohistochemistry; inflammatory markers; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury by attenuation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis.J Neurosurg Spine. 2016 Jun;24(6):949-59. doi: 10.3171/2015.10.SPINE15612. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Neurosurg Spine. 2016. PMID: 26871652
-
Thymoquinone blocks lung injury and fibrosis by attenuating bleomycin-induced oxidative stress and activation of nuclear factor Kappa-B in rats.Toxicology. 2012 Dec 16;302(2-3):106-13. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Toxicology. 2012. PMID: 22982510
-
Thymoquinone Abrogates Acrylamide-Induced Cerebellar Toxicity via Modulation of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling, Oxidative Neuroinflammation, and Neuroapoptosis in Rats.J Med Food. 2024 Nov;27(11):1062-1069. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2023.0228. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Med Food. 2024. PMID: 39321097
-
Thymoquinone, a major constituent in Nigella sativa seeds, is a potential preventative and treatment option for atherosclerosis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 15;909:174420. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174420. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34391767 Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Thymoquinone and Its Nanoformulations in Pulmonary Injury: A Comprehensive Review.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jul 27;16:5117-5131. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S314321. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34349511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Study on dietary intake, risk assessment, and molecular toxicity mechanism of benzo[α]pyrene in college students in China Bashu area.Food Sci Nutr. 2022 Aug 9;10(12):4155-4167. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3007. eCollection 2022 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36514765 Free PMC article.
-
3,4-Dihydroxyphenylethanol (DPE or Hydroxytyrosol) Counteracts ERK1/2 and mTOR Activation, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release, Autophagy and Mitophagy Reduction Mediated by Benzo[a]pyrene in Primary Human Colonic Epithelial Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Mar 17;14(3):663. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14030663. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35336037 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone enhances the antioxidant and anticancer activity of Lebanese propolis.World J Clin Oncol. 2023 May 24;14(5):203-214. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v14.i5.203. World J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37275937 Free PMC article.
-
Nigella sativa: A Comprehensive Review of Its Therapeutic Potential, Pharmacological Properties, and Clinical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 14;25(24):13410. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413410. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective effects of Nigella sativa oil, thymoquinone and dexamethasone on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats.Vet Res Forum. 2024;15(11):613-620. doi: 10.30466/vrf.2024.2024154.4196. Epub 2024 Nov 15. Vet Res Forum. 2024. PMID: 39807395 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

