SARS-CoV-2: One Year in the Pandemic. What Have We Learned, the New Vaccine Era and the Threat of SARS-CoV-2 Variants
- PMID: 34072088
- PMCID: PMC8226851
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9060611
SARS-CoV-2: One Year in the Pandemic. What Have We Learned, the New Vaccine Era and the Threat of SARS-CoV-2 Variants
Abstract
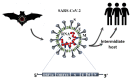
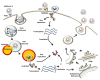
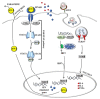
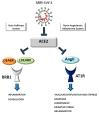
Since the beginning of 2020, the new pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 and named coronavirus disease 19 (COVID 19) has changed our socio-economic life. In just a few months, SARS-CoV-2 was able to spread worldwide at an unprecedented speed, causing hundreds of thousands of deaths, especially among the weakest part of the population. Indeed, especially at the beginning of this pandemic, many reports highlighted how people, suffering from other pathologies, such as hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes, are more at risk of severe outcomes if infected. Although this pandemic has put the entire academic world to the test, it has also been a year of intense research and many important contributions have advanced our understanding of SARS-CoV-2 origin, its molecular structure and its mechanism of infection. Unfortunately, despite this great effort, we are still a long way from fully understanding how SARS-CoV-2 dysregulates organismal physiology and whether the current vaccines will be able to protect us from possible future pandemics. Here, we discuss the knowledge we have gained during this year and which questions future research should address.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID19; SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus; kinin-kallikrein system; renin angiotensin aldosterone system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

