Molecular Insights into the Role of Cysteine-Rich Peptides in Induced Resistance to Fusarium oxysporum Infection in Tomato Based on Transcriptome Profiling
- PMID: 34072144
- PMCID: PMC8198727
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115741
Molecular Insights into the Role of Cysteine-Rich Peptides in Induced Resistance to Fusarium oxysporum Infection in Tomato Based on Transcriptome Profiling
Abstract
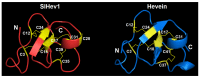
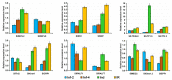
Cysteine-rich peptides (CRPs) play an important role in plant physiology. However, their role in resistance induced by biogenic elicitors remains poorly understood. Using whole-genome transcriptome sequencing and our CRP search algorithm, we analyzed the repertoire of CRPs in tomato Solanum lycopersicum L. in response to Fusarium oxysporum infection and elicitors from F. sambucinum. We revealed 106 putative CRP transcripts belonging to different families of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), signaling peptides (RALFs), and peptides with non-defense functions (Major pollen allergen of Olea europaea (Ole e 1 and 6), Maternally Expressed Gene (MEG), Epidermal Patterning Factor (EPF)), as well as pathogenesis-related proteins of families 1 and 4 (PR-1 and 4). We discovered a novel type of 10-Cys-containing hevein-like AMPs named SlHev1, which was up-regulated both by infection and elicitors. Transcript profiling showed that F. oxysporum infection and F. sambucinum elicitors changed the expression levels of different overlapping sets of CRP genes, suggesting the diversification of functions in CRP families. We showed that non-specific lipid transfer proteins (nsLTPs) and snakins mostly contribute to the response of tomato plants to the infection and the elicitors. The involvement of CRPs with non-defense function in stress reactions was also demonstrated. The results obtained shed light on the mode of action of F. sambucinum elicitors and the role of CRP families in the immune response in tomato.
Keywords: F. sambucinum; Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici; Solanum lycopersicum L.; antimicrobial peptides; cysteine-rich peptides; elicitors; high-throughput transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq); plant immunity; signaling peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures











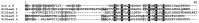




Similar articles
-
Identification of I-7 expands the repertoire of genes for resistance to Fusarium wilt in tomato to three resistance gene classes.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Apr;17(3):448-63. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12294. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26177154 Free PMC article.
-
Tomato immune receptor Ve1 recognizes effector of multiple fungal pathogens uncovered by genome and RNA sequencing.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Mar 27;109(13):5110-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119623109. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22416119 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-Based Analysis of Tomato Genotypes Resistant to Bacterial Spot (Xanthomonas perforans) Race T4.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 6;21(11):4070. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114070. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32517212 Free PMC article.
-
The arms race between tomato and Fusarium oxysporum.Mol Plant Pathol. 2010 Mar;11(2):309-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2009.00605.x. Mol Plant Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20447279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breeding for Resistance to Fusarium Wilt of Tomato: A Review.Genes (Basel). 2021 Oct 23;12(11):1673. doi: 10.3390/genes12111673. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fungi That Promote Plant Growth in the Rhizosphere Boost Crop Growth.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;9(2):239. doi: 10.3390/jof9020239. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptides in plant-microbe interactions: Functional diversity and pharmacological applications.Cell Surf. 2025 May 15;13:100145. doi: 10.1016/j.tcsw.2025.100145. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cell Surf. 2025. PMID: 40486090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Genes Encoding Defense-Related Peptides of Filipendula ulmaria in Response to Bipolaris sorokiniana Infection.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Mar 28;10(4):258. doi: 10.3390/jof10040258. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38667929 Free PMC article.
-
Carboxypeptidase inhibitors from Solanaceae as a new subclass of pathogenesis related peptide aiming biotechnological targets for plant defense.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Nov 16;10:1259026. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1259026. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 38033385 Free PMC article.
-
The γ-Core Motif Peptides of Plant AMPs as Novel Antimicrobials for Medicine and Agriculture.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 28;24(1):483. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010483. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

