Psychological Distress of Metastatic Melanoma Patients during Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Results of a Prospective Study
- PMID: 34072206
- PMCID: PMC8198252
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112642
Psychological Distress of Metastatic Melanoma Patients during Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Results of a Prospective Study
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) provide effective treatment options for advanced melanoma patients. However, they are associated with high rates of immune-related side effects. There are no data on the distress of melanoma patients during their ICI treatment. We, therefore, conducted a prospective longitudinal study to assess distress and the need for psycho-oncological support in these patients.
Methods: Questionnaires were completed before initiation of ICI (T0), after 6-8 weeks (T1), and after 12-14 weeks (T2). We furthermore included the Hornheide Screening Instrument (HSI), distress thermometer (DT), and patients' self-assessment. Binary logistic regression was performed to identify factors indicating a need for psychooncological support.
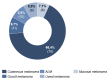
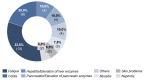
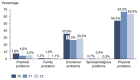
Results: 36.3%/55.8% (HSI / DT) of the patients were above the threshold, indicating a need for psychooncological support at T0, and 7.8% of the patients reported practical problems. In contrast, at T2, the distress values had decreased to 29.0%/40.2% (HSI/DT), respectively. Female gender and occurrence of side effects significantly correlated to values above the threshold. The strongest factor was the patient's self-assessment.
Conclusion: With the beginning of ICI, psychooncological support should be offered. Furthermore, practical problems should be considered, e.g., transport to therapy. Female patients and patients with side effects should be given special attention, as well as the patient self-assessment.
Keywords: checkpoint inhibitors; distress; dt; his; immune therapy; metastatic melanoma; problems; psychooncology.
Conflict of interest statement
A.F. served as a consultant to Roche, Novartis, MSD, BMS, Pierre-Fabre; received travel support from Roche, Novartis, BMS, Pierre-Fabre, received speaker fees from Roche, Novartis, BMS, MSD, and CeGaT, outside the submitted work. She reports institutional research grants from BMS Stiftung Immunonkologie outside the submitted work. T.E. reports personal fees from Amgen, grants and personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Philogen, grants, and personal fees from Roche, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from MSD, outside the submitted work. C.G. reports personal fees from Amgen, grants and personal fees from NeraCare, grants and personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Philogen, grants and personal fees from Roche, grants and personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from BMS, personal fees from MSD, outside the submitted work. The other authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distress and Its Determinants in 820 Consecutive Melanoma Patients.Cancer Med. 2025 Mar;14(6):e70820. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70820. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40125560 Free PMC article.
-
The need for psycho-oncological support for melanoma patients: Central role of patients' self-evaluation.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Sep;96(37):e7987. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007987. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28906378 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the need for psychooncological support: screening instruments in combination with patients' subjective evaluation may define psychooncological pathways.Psychooncology. 2015 Dec;24(12):1784-91. doi: 10.1002/pon.3855. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Psychooncology. 2015. PMID: 26042392
-
Focusing on cancer patients' intentions to use psychooncological support: A longitudinal, mixed-methods study.Psychooncology. 2018 Jun;27(6):1656-1663. doi: 10.1002/pon.4735. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Psychooncology. 2018. PMID: 29656415 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors and targeted therapy on health-related quality of life of people with stage III and IV melanoma: a mixed-methods systematic review.Eur J Cancer. 2023 May;184:83-105. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2023.02.005. Epub 2023 Feb 18. Eur J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36907021
Cited by
-
Distress and Its Determinants in 820 Consecutive Melanoma Patients.Cancer Med. 2025 Mar;14(6):e70820. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70820. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40125560 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term survival of stage IV melanoma patients: evaluation on 640 melanoma patients entering stage IV between 2014 and 2017.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Jan 18;150(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05533-0. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38238578 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Resistance to Immunotherapy: Comprehensive Insights with Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Apr 4;15(4):1143. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041143. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survivorship outcomes in patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a scoping review.J Cancer Surviv. 2025 Jun;19(3):806-845. doi: 10.1007/s11764-023-01507-w. Epub 2024 Jan 4. J Cancer Surviv. 2025. PMID: 38175366 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of life under treatment with the immune checkpoint inhibitors ipilimumab and nivolumab in melanoma patients. Real-world data from a prospective observational study at the Skin Cancer Center Kiel.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Oct 10;150(10):454. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05981-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39387946 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forschner A., Riedel P., Gassenmaier M., Scheu A., Kofler L., Garbe C., Schäffeler N., Mayer S., Eigentler T.K. The demand for psycho-oncological support in 820 melanoma patients: What are the determinants for the development of distress? JCO. 2017;35(Suppl. 15):9514. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.9514. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources