HSV-1 and Endogenous Retroviruses as Risk Factors in Demyelination
- PMID: 34072259
- PMCID: PMC8199333
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115738
HSV-1 and Endogenous Retroviruses as Risk Factors in Demyelination
Abstract
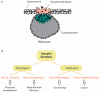
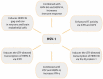
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) is a neurotropic alphaherpesvirus that can infect the peripheral and central nervous systems, and it has been implicated in demyelinating and neurodegenerative processes. Transposable elements (TEs) are DNA sequences that can move from one genomic location to another. TEs have been linked to several diseases affecting the central nervous system (CNS), including multiple sclerosis (MS), a demyelinating disease of unknown etiology influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Exogenous viral transactivators may activate certain retrotransposons or class I TEs. In this context, several herpesviruses have been linked to MS, and one of them, HSV-1, might act as a risk factor by mediating processes such as molecular mimicry, remyelination, and activity of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs). Several herpesviruses have been involved in the regulation of human ERVs (HERVs), and HSV-1 in particular can modulate HERVs in cells involved in MS pathogenesis. This review exposes current knowledge about the relationship between HSV-1 and human ERVs, focusing on their contribution as a risk factor for MS.
Keywords: demyelination; endogenous retroviruses; herpes simplex virus type 1; herpesviruses; multiple sclerosis; transposable elements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roizman B., Knipe D.M., Whitley R. Herpes simplex viruses. In: Howley D.M.K.a.P.M., editor. Fields Virology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2007. pp. 2501–2601.
-
- Wald A., Corey L. Persistence in the population: Epidemiology, transmission. In: Arvin A., Campadelli-Fiume G., Mocarski E., Moore P.S., Roizman B., Whitley R., Yamanishi K., editors. Human Herpesviruses: Biology, Therapy, and Immunoprophylaxis. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

