Structural and Functional Modulation of Perineuronal Nets: In Search of Important Players with Highlight on Tenascins
- PMID: 34072323
- PMCID: PMC8230358
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10061345
Structural and Functional Modulation of Perineuronal Nets: In Search of Important Players with Highlight on Tenascins
Abstract
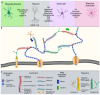
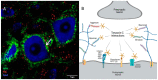
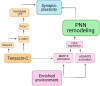
The extracellular matrix (ECM) of the brain plays a crucial role in providing optimal conditions for neuronal function. Interactions between neurons and a specialized form of ECM, perineuronal nets (PNN), are considered a key mechanism for the regulation of brain plasticity. Such an assembly of interconnected structural and regulatory molecules has a prominent role in the control of synaptic plasticity. In this review, we discuss novel ways of studying the interplay between PNN and its regulatory components, particularly tenascins, in the processes of synaptic plasticity, mechanotransduction, and neurogenesis. Since enhanced neuronal activity promotes PNN degradation, it is possible to study PNN remodeling as a dynamical change in the expression and organization of its constituents that is reflected in its ultrastructure. The discovery of these subtle modifications is enabled by the development of super-resolution microscopy and advanced methods of image analysis.
Keywords: extracellular matrix; mechanotransduction; neurogenesis; perineuronal nets; super-resolution microscopy; synaptic plasticity; tenascin-C.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Chemorepulsive Protein Semaphorin 3A and Perineuronal Net-Mediated Plasticity.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:3679545. doi: 10.1155/2016/3679545. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27057361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experience-dependent development of perineuronal nets and chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan receptors in mouse visual cortex.Matrix Biol. 2013 Aug 8;32(6):352-63. doi: 10.1016/j.matbio.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Matrix Biol. 2013. PMID: 23597636
-
The hyaluronan and proteoglycan link proteins: Organizers of the brain extracellular matrix and key molecules for neuronal function and plasticity.Exp Neurol. 2015 Dec;274(Pt B):134-44. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Sep 24. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26387938 Review.
-
Experience-dependent plasticity and modulation of growth regulatory molecules at central synapses.PLoS One. 2011 Jan 31;6(1):e16666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016666. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21304956 Free PMC article.
-
Perineuronal Nets: From Structure to Neurological Disorders.Curr Med Chem. 2025;32(9):1685-1701. doi: 10.2174/0109298673258290231009111633. Curr Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 37946343 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Perineuronal Nets in Physiology and Disease: Insights from Recent Studies.Cells. 2025 Feb 20;14(5):321. doi: 10.3390/cells14050321. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40072050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formation of perineuronal nets within a thalamocortical circuit shapes mechanical and thermal pain thresholds in mice with neuropathic pain.Pain. 2025 May 1;166(5):1128-1142. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003563. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Pain. 2025. PMID: 40112162 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Cerebellar Intrinsic Neuronal Excitability, Synaptic Plasticity, and Perineuronal Nets in Eyeblink Conditioning.Biology (Basel). 2024 Mar 21;13(3):200. doi: 10.3390/biology13030200. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brevican, Neurocan, Tenascin-C, and Tenascin-R Act as Important Regulators of the Interplay Between Perineuronal Nets, Synaptic Integrity, Inhibitory Interneurons, and Otx2.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 2;10:886527. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.886527. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35721494 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between astrocytes and extracellular matrix structures contribute to neuroinflammation-associated epilepsy pathology.Front Mol Med. 2023 Jun 14;3:1198021. doi: 10.3389/fmmed.2023.1198021. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 39086689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Golgi C. Intorno Alla Struttura Della Cellula Nervosa. Boll. Della Soc. Med. -Chir. Di Pavia. 1898;13:316.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

