Social Behavior and Ultrasonic Vocalizations in a Genetic Rat Model Haploinsufficient for the Cross-Disorder Risk Gene Cacna1c
- PMID: 34072335
- PMCID: PMC8229447
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci11060724
Social Behavior and Ultrasonic Vocalizations in a Genetic Rat Model Haploinsufficient for the Cross-Disorder Risk Gene Cacna1c
Abstract
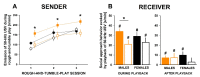
The top-ranked cross-disorder risk gene CACNA1C is strongly associated with multiple neuropsychiatric dysfunctions. In a recent series of studies, we applied a genomically informed approach and contributed extensively to the behavioral characterization of a genetic rat model haploinsufficient for the cross-disorder risk gene Cacna1c. Because deficits in processing social signals are associated with reduced social functioning as commonly seen in neuropsychiatric disorders, we focused on socio-affective communication through 22-kHz and 50-kHz ultrasonic vocalizations (USV). Specifically, we applied a reciprocal approach for studying socio-affective communication in sender and receiver by including rough-and-tumble play and playback of 22-kHz and 50-kHz USV. Here, we review the findings obtained in this recent series of studies and link them to the key features of 50-kHz USV emission during rough-and-tumble play and social approach behavior evoked by playback of 22-kHz and 50-kHz USV. We conclude that Cacna1c haploinsufficiency in rats leads to robust deficits in socio-affective communication through 22-kHz and 50-kHz USV and associated alterations in social behavior, such as rough-and-tumble play behavior.
Keywords: Cav1.2; alarm call; animal model; calcium; playback; rough-and-tumble play; social approach; social contact call; social play; ultrasonic vocalization.
Conflict of interest statement
M.W. is scientific advisor of Avisoft Bioacoustics. The other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Green E.K., Grozeva D., Jones I., Jones L., Kirov G., Caesar S., Gordon-Smith K., Fraser C., Forty L., Russell E., et al. The bipolar disorder risk allele at CACNA1C also confers risk of recurrent major depression and of schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry. 2010;15:1016–1022. doi: 10.1038/mp.2009.49. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferreira M.A., O’Donovan M.C., Meng Y.A., Jones I.R., Ruderfer D.M., Jones L., Fan J., Kirov G., Perlis R.H., Green E.K., et al. Collaborative genome-wide association analysis supports a role for ANK3 and CACNA1C in bipolar disorder. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:1056–1058. doi: 10.1038/ng.209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Splawski I., Timothy K.W., Sharpe L.M., Decher N., Kumar P., Bloise R., Napolitano C., Schwartz P.J., Joseph R.M., Condouris K., et al. Ca(V)1.2 calcium channel dysfunction causes a multisystem disorder including arrhythmia and autism. Cell. 2004;119:19–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.011. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

