Heparin-Binding Protein 17/Fibroblast Growth Factor-Binding Protein-1 Knockout Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Differentiation of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 34072393
- PMCID: PMC8199440
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112684
Heparin-Binding Protein 17/Fibroblast Growth Factor-Binding Protein-1 Knockout Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Differentiation of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
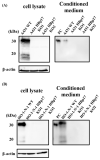
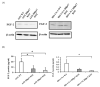
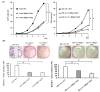
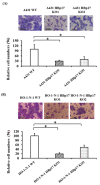
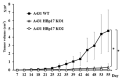
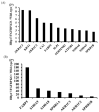
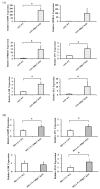
Heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1) has been observed to induce the tumorigenic potential of epithelial cells and is highly expressed in oral cancer cell lines and tissues. It is also recognized as a pro-angiogenic molecule because of its interaction with fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2. In this study, we examined the functional role of HBp17/FGFBP-1 in A431 and HO-1-N-1 cells. Originally, HBp17/FGFBP-1 was purified from A431 cell-conditioned media based on its capacity to bind to FGF-1 and FGF-2. We isolated and established HBp17/FGFBP-1-knockout (KO)-A431 and KO-HO-1-N-1 cell lines using the clusters of regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) and CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9) gene editing technology. The amount of FGF-2 secreted into conditioned medium decreased for A431-HBp17-KO and HO-1-N-1-HBp17-KO cells compared to their WT counterparts. Functional assessment showed that HBp17/FGFBP-1 KO inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation, and cell motility in vitro. It also inhibited tumor growth in vivo compared to controls, which confirmed the significant difference in growth in vitro between HBp17-KO cells and wild-type (WT) cells, indicating that HBp17/FGFBP-1 is a potent therapeutic target in squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC). In addition, complementary DNA/protein expression analysis followed by Gene Ontology and protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis using the Database for Visualization and Integrated Discovery and Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes/Proteins showed that both gene and protein expression related to epidermal development, cornification, and keratinization were upregulated in A431-HBp17-KO and HO-1-N-1-KO cells. This is the first discovery of a novel role of HBp17/FGFBP-1 that regulates SCC and OSCC cell differentiation.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; FGF-2; HBp17/FGFBP-1; cell differentiation; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential treatment of squamous cell carcinoma by targeting heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein 1 with vitamin D3 or eldecalcitol.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 Jun;60(6):583-589. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00913-3. Epub 2024 May 7. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38713345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eldecalcitol (ED-71)-induced exosomal miR-6887-5p suppresses squamous cell carcinoma cell growth by targeting heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1).In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020 Mar;56(3):222-233. doi: 10.1007/s11626-020-00440-x. Epub 2020 Mar 17. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2020. PMID: 32185608
-
Eldecalcitol (ED-71), an analog of 1α,25(OH)2D3, inhibits the growth of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) cells in vitro and in vivo by down-regulating expression of heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein-1 (HBp17/FGFBP-1) and FGF-2.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2017 Oct;53(9):810-817. doi: 10.1007/s11626-017-0183-9. Epub 2017 Jul 14. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2017. PMID: 28710602
-
1α,25(OH)₂D₃ inhibits FGF-2 release from oral squamous cell carcinoma cells through down-regulation of HBp17/FGFBP-1.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014 Oct;50(9):802-6. doi: 10.1007/s11626-014-9787-5. Epub 2014 Jun 18. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2014. PMID: 24938357
-
1α,25OH2D3 down-regulates HBp17/FGFBP-1 expression via NF-κB pathway.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013 Jul;136:98-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.10.011. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23104116 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics as a tool to improve novel insights into skin diseases: what we know and where we should be going.Front Surg. 2022 Oct 21;9:1025557. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1025557. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 36338621 Free PMC article.
-
Serine protease PRSS23 drives gastric cancer by enhancing tumor associated macrophage infiltration via FGF2.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 15;13:955841. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955841. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189305 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the mechanisms of angiogenesis in hepatoblastoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 May 14;13:1535339. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1535339. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40438141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical significance of integrin αV and β superfamily members and focal adhesion kinase activity in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a retrospective observational study.Pathol Oncol Res. 2024 Jan 18;30:1611571. doi: 10.3389/pore.2024.1611571. eCollection 2024. Pathol Oncol Res. 2024. PMID: 38312516 Free PMC article.
-
Potential treatment of squamous cell carcinoma by targeting heparin-binding protein 17/fibroblast growth factor-binding protein 1 with vitamin D3 or eldecalcitol.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 Jun;60(6):583-589. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00913-3. Epub 2024 May 7. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38713345 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

