Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate: Is There Any Scientific Evidence for Their Effectiveness as Disease-Modifying Drugs in Knee Osteoarthritis Preclinical Studies?-A Systematic Review from 2000 to 2021
- PMID: 34072407
- PMCID: PMC8228516
- DOI: 10.3390/ani11061608
Glucosamine and Chondroitin Sulfate: Is There Any Scientific Evidence for Their Effectiveness as Disease-Modifying Drugs in Knee Osteoarthritis Preclinical Studies?-A Systematic Review from 2000 to 2021
Abstract
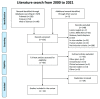
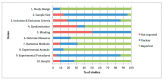
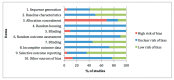
Glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate have been proposed due to their physiological and functional benefits in the management of osteoarthritis in companion animals. However, the scientific evidence for their use is still controversial. The purpose of this review was to critically elucidate the efficacy of these nutraceutical therapies in delaying the progression of osteoarthritis, evaluating their impact on the synovial knee joint tissues and biochemical markers in preclinical studies by systematically reviewing the last two decades of peer-reviewed publications on experimental osteoarthritis. Three databases (PubMed, Scopus and, Web of Science) were screened for eligible studies. Twenty-two articles were included in the review. Preclinical studies showed a great heterogeneity among the experimental designs and their outcomes. Generally, the evaluated nutraceuticals, alone or in combination, did not seem to prevent the subchondral bone changes, the synovial inflammation or the osteophyte formation. However, further experimental studies may be needed to evaluate their effect at those levels. Regarding the cartilage status and biomarkers, positive responses were identified in approximately half of the evaluated articles. Furthermore, beneficial effects were associated with the pre-emptive administrations, higher doses and, multimodality approaches with some combined therapies. However, additional studies in the long term and with good quality and systematic design are required.
Keywords: animal models; biochemical markers; cartilage; chondroitin sulfate; glucosamine; nutraceuticals; osteoarthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson K.L., O’Neill D.G., Brodbelt D.C., Church D.B., Meeson R.L., Sargan D., Summers J.F., Zulch H., Collins L.M. Prevalence, duration and risk factors for appendicular osteoarthritis in a UK dog population under primary veterinary care. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23940-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

