Congested Crowd Counting via Adaptive Multi-Scale Context Learning
- PMID: 34072408
- PMCID: PMC8198824
- DOI: 10.3390/s21113777
Congested Crowd Counting via Adaptive Multi-Scale Context Learning
Abstract
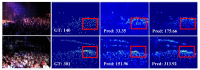
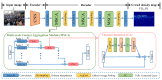
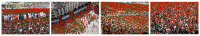
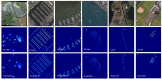
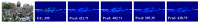
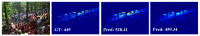
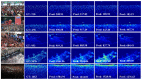
In this paper, we propose a novel congested crowd counting network for crowd density estimation, i.e., the Adaptive Multi-scale Context Aggregation Network (MSCANet). MSCANet efficiently leverages the spatial context information to accomplish crowd density estimation in a complicated crowd scene. To achieve this, a multi-scale context learning block, called the Multi-scale Context Aggregation module (MSCA), is proposed to first extract different scale information and then adaptively aggregate it to capture the full scale of the crowd. Employing multiple MSCAs in a cascaded manner, the MSCANet can deeply utilize the spatial context information and modulate preliminary features into more distinguishing and scale-sensitive features, which are finally applied to a 1 × 1 convolution operation to obtain the crowd density results. Extensive experiments on three challenging crowd counting benchmarks showed that our model yielded compelling performance against the other state-of-the-art methods. To thoroughly prove the generality of MSCANet, we extend our method to two relevant tasks: crowd localization and remote sensing object counting. The extension experiment results also confirmed the effectiveness of MSCANet.
Keywords: crowd counting; crowd density estimation; crowd localization; multi-scale context learning; remote sensing object counting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
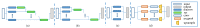
References
-
- Fortino G., Savaglio C., Spezzano G., Zhou M. Internet of Things as System of Systems: A Review of Methodologies, Frameworks, Platforms, and Tools. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.3042898. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

