Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine "PoliovacSin": Clinical Trials Phase I and II
- PMID: 34072466
- PMCID: PMC8229617
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9060565
Immunogenicity and Safety of Inactivated Sabin-Strain Polio Vaccine "PoliovacSin": Clinical Trials Phase I and II
Abstract
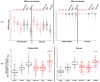
Global polio eradication requires both safe and effective vaccines, and safe production processes. Sabin oral poliomyelitis vaccine (OPV) strains can evolve to virulent viruses and result in poliomyelitis outbreaks, and conventional inactivated poliomyelitis vaccine (Salk-IPV) production includes accumulation of large stocks of neurovirulent wild polioviruses. Therefore, IPV based on attenuated OPV strains seems a viable option. To increase the global supply of affordable inactivated vaccine in the still not-polio free world we developed an IPV made from the Sabin strains-PoliovacSin. Clinical trials included participants 18-60 years of age. A phase I single-center, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial included 60 participants, who received one dose of PoliovacSin or Placebo. A phase II multicenter, randomized, double-blind, comparative clinical trial included 200 participants, who received one dose of PoliovacSin or Imovax Polio. All vaccinations were well tolerated, and PoliovacSin had a comparable safety profile to the Placebo or the reference Imovax Polio preparations. A significant increase in neutralizing antibody levels to polioviruses types 1-3 (Sabin and wild) was observed in PoliovacSin and Imovax Polio vaccinated groups. Therefore, clinical trials confirmed good tolerability, low reactogenicity, and high safety profile of the PoliovacSin and its pronounced immunogenic properties. The preparation was approved for clinical trials involving infants.
Keywords: IPV; Sabin strain; clinical trial; inactivated vaccine; poliovirus.
Conflict of interest statement
FSBSI “Chumakov FSC R&D IBP RAS” is a polio vaccine producer. AP, GI, YI, AK, AI, ASh, LA, YK, ASin and AI work for the manufacturing unit. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of experimental stand-alone trivalent, inactivated Sabin-strain polio vaccine formulations in healthy infants: A randomized, observer-blind, controlled phase 1/2 trial.Vaccine. 2020 Jul 14;38(33):5313-5323. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.05.081. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32563609 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of two novel type 2 oral poliovirus vaccine candidates compared with a monovalent type 2 oral poliovirus vaccine in healthy adults: two clinical trials.Lancet. 2021 Jan 2;397(10268):39-50. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32541-1. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Lancet. 2021. PMID: 33308429 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The safety and immunogenicity of two novel live attenuated monovalent (serotype 2) oral poliovirus vaccines in healthy adults: a double-blind, single-centre phase 1 study.Lancet. 2019 Jul 13;394(10193):148-158. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31279-6. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31174831 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development and introduction of inactivated poliovirus vaccines derived from Sabin strains in Japan.Vaccine. 2016 Apr 7;34(16):1975-85. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.11.015. Epub 2014 Nov 21. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 25448090 Review.
-
Development of inactivated poliovirus vaccine from Sabin strains: A progress report.Biologicals. 2016 Nov;44(6):581-587. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2016.08.005. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Biologicals. 2016. PMID: 27720268 Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective Technologies of Vaccination: Do We Still Need Old Vaccines?Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;10(6):891. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10060891. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746498 Free PMC article.
-
An Inactivated West Nile Virus Vaccine Candidate Based on the Lineage 2 Strain.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;12(12):1398. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12121398. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39772058 Free PMC article.
-
Intensification of Vero cell adherence to microcarrier particles during cultivation in a wave bioreactor.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 14;13:1542060. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1542060. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40028290 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and immunogenicity of 3 formulations of a Sabin inactivated poliovirus vaccine produced on the PER.C6® cell line: A phase 2, double-blind, randomized, controlled study in infants vaccinated at 6, 10 and 14 weeks of age.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022 Nov 30;18(5):2044255. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2022.2044255. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2022. PMID: 35344464 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Basic and Applied Sciences: Technology and Immunobiological Products.Her Russ Acad Sci. 2022;92(4):452-455. doi: 10.1134/S101933162204013X. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Her Russ Acad Sci. 2022. PMID: 36091846 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peter F., Wright R.J., Kim-Farley C.A., de Quadros S.E., Robertson R.M.N., Scott N.A. Ward and Ralph, H. Henderson. Strategies for the global eradication of poliomyelitis by the year 2000. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991;325:1774–1779. - PubMed
-
- Sutter R.W., Kew O.M., Cochi S.L., Aylward R.B. Poliovirus vaccine—Live. In: Plotkin S.A., Orenstein W.A., Offit P.A., Edwards K.M., editors. Vaccines. 7th ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2018. pp. 866–916.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Transmission of wild poliovirus type 2—Apparent global interruption. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2001;76:95–97. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

