Aging-Related Metabolic Dysfunction in the Salivary Gland: A Review of the Literature
- PMID: 34072470
- PMCID: PMC8198609
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115835
Aging-Related Metabolic Dysfunction in the Salivary Gland: A Review of the Literature
Abstract
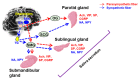
Aging-related salivary dysfunction commonly induces the poor oral health, including decreased saliva flow and dental caries. Although the clinical significance of the salivary glands is well-known, the complex metabolic pathways contributing to the aging-dysfunction process are only beginning to be uncovered. Here, we provide a comprehensive overview of the metabolic changes in aging-mediated salivary gland dysfunction as a key aspect of oral physiology. Several metabolic neuropeptides or hormones are involved in causing or contributing to salivary gland dysfunction, including hyposalivation and age-related diseases. Thus, aging-related metabolism holds promise for early diagnosis, increased choice of therapy and the identification of new metabolic pathways that could potentially be targeted in salivary gland dysfunction.
Keywords: aging; dysfunction; metabolism; saliva; salivary glands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gene transfer to salivary glands.Int Rev Cytol. 2002;213:93-146. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(02)13013-0. Int Rev Cytol. 2002. PMID: 11837896 Review.
-
Diagnostic aspects of salivary gland disorders.Ann Clin Res. 1973 Dec;5(6):357-64. Ann Clin Res. 1973. PMID: 4599893 Review. No abstract available.
-
Prosthodontic implications of saliva and salivary gland dysfunction.J Prosthodont. 2023 Dec;32(9):766-775. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13725. Epub 2023 Jul 6. J Prosthodont. 2023. PMID: 37302138 Review.
-
Therapy-induced dysfunction of salivary glands: implications for oral health.Spec Care Dentist. 1985 Nov-Dec;5(6):274-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1754-4505.1985.tb00593.x. Spec Care Dentist. 1985. PMID: 3911461 No abstract available.
-
Metabolic remodeling triggered by salivation and diabetes in major salivary glands.NMR Biomed. 2017 Feb;30(2). doi: 10.1002/nbm.3683. Epub 2016 Dec 26. NMR Biomed. 2017. PMID: 28025847
Cited by
-
The Oral Microbial Ecosystem in Age-Related Xerostomia: A Critical Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 28;25(23):12815. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312815. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in histology of the aging salivary gland and correlation with the glandular inflammatory microenvironment.iScience. 2023 Apr 5;26(5):106571. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106571. eCollection 2023 May 19. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37124415 Free PMC article.
-
The zinc receptor, ZnR/GPR39, modulates taste sensitivity by regulating ion secretion in mouse salivary gland.iScience. 2025 Jan 28;28(2):111912. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.111912. eCollection 2025 Feb 21. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40017509 Free PMC article.
-
Caries risk factors among Indonesian adults: insights from the national health survey.Braz Oral Res. 2025 Feb 24;39:e025. doi: 10.1590/1807-3107bor-2025.vol39.025. eCollection 2025. Braz Oral Res. 2025. PMID: 40008739 Free PMC article.
-
Practice and challenge of age-friendly functional restoration of stomatognathic system based on the strategy of functional tooth loss.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Feb 1;43(1):15-27. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2025.2024188. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 39840622 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
References
-
- Ekström J., Khosravani N., Castagnola M., Messana I. Saliva and the control of its secretion. In: Ekberg O., editor. Dysphagia. Medical Radiology. Springer; Cham, Switzerland: 2017.
-
- Nassar M., Hiraishi N., Islam M.S., Otsuki M., Tagami J. Age-Related changes in salivary biomarkers. J. Dent. Sci. 2014;9:85–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2013.11.002. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

