The Effects of Chemical and Mechanical Stresses on Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas fluorescens Single- and Dual-Species Biofilm Removal
- PMID: 34072497
- PMCID: PMC8228086
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9061174
The Effects of Chemical and Mechanical Stresses on Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas fluorescens Single- and Dual-Species Biofilm Removal
Abstract
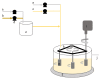
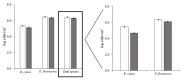
Biofilm control is mainly based on chemical disinfection, without a clear understanding of the role of the biocides and process conditions on biofilm removal. This study aims to understand the effects of a biocide (benzyldimethyldodecyl ammonium chloride-BDMDAC) and mechanical treatment (an increase of shear stress -τw) on single- and dual-species biofilms formed by Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas fluorescens on high-density polyethene (HDPE). BDMDAC effects were initially assessed on bacterial physicochemical properties and initial adhesion ability. Then, mature biofilms were formed on a rotating cylinder reactor (RCR) for 7 days to assess the effects of chemical and mechanical treatments, and the combination of both on biofilm removal. The results demonstrated that the initial adhesion does not predict the formation of mature biofilms. It was observed that the dual-species biofilms were the most susceptible to BDMDAC exposure. The exposure to increasing τw emphasised the mechanical stability of biofilms, as lower values of τw (1.66 Pa) caused high biofilm erosion and higher τw values (17.7 Pa) seem to compress the remaining biofilm. In general, the combination of BDMDAC and the mechanical treatment was synergic in increasing biofilm removal. However, these were insufficient to cause total biofilm removal (100%; an average standard deviation of 11% for the method accuracy should be considered) from HDPE.
Keywords: BDMDAC; disinfection; high-density polyethene; rotating cylinder reactor; shear stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biofilm formation under high shear stress increases resilience to chemical and mechanical challenges.Biofouling. 2022 Jan;38(1):1-12. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2021.2006189. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Biofouling. 2022. PMID: 34818957
-
The effects of glutaraldehyde on the control of single and dual biofilms of Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas fluorescens.Biofouling. 2011 Mar;27(3):337-46. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2011.575935. Biofouling. 2011. PMID: 21512918
-
The action of chemical and mechanical stresses on single and dual species biofilm removal of drinking water bacteria.Sci Total Environ. 2018 Aug 1;631-632:987-993. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.03.042. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Sci Total Environ. 2018. PMID: 29728008
-
Species association increases biofilm resistance to chemical and mechanical treatments.Water Res. 2009 Jan;43(1):229-37. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.10.010. Epub 2008 Oct 18. Water Res. 2009. PMID: 18977505
-
[Biofilms and Oxidizing Biocides; Evaluation of Disinfection and Removal Effects by Using Established Microbial Systems].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(6):707-717. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.16-00254. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017. PMID: 28566577 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Persister Biofilm Cells of Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas fluorescens.Microorganisms. 2022 Jan 13;10(1):160. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10010160. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35056610 Free PMC article.
-
Multispecies Bacterial Biofilms and Their Evaluation Using Bioreactors.Foods. 2023 Dec 15;12(24):4495. doi: 10.3390/foods12244495. Foods. 2023. PMID: 38137299 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fernandes S., Gomes I.B., Simões L.C., Simões M. Overview on the hydrodynamic conditions found in industrial systems and its impact in (bio)fouling formation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021;418:129348. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.129348. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

