The Evolution of Rag Gene Enhancers and Transcription Factor E and Id Proteins in the Adaptive Immune System
- PMID: 34072618
- PMCID: PMC8199221
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115888
The Evolution of Rag Gene Enhancers and Transcription Factor E and Id Proteins in the Adaptive Immune System
Abstract
Adaptive immunity relies on the V(D)J DNA recombination of immunoglobulin (Ig) and T cell receptor (TCR) genes, which enables the recognition of highly diverse antigens and the elicitation of antigen-specific immune responses. This process is mediated by recombination-activating gene (Rag) 1 and Rag2 (Rag1/2), whose expression is strictly controlled in a cell type-specific manner; the expression of Rag1/2 genes represents a hallmark of lymphoid lineage commitment. Although Rag genes are known to be evolutionally conserved among jawed vertebrates, how Rag genes are regulated by lineage-specific transcription factors (TFs) and how their regulatory system evolved among vertebrates have not been fully elucidated. Here, we reviewed the current body of knowledge concerning the cis-regulatory elements (CREs) of Rag genes and the evolution of the basic helix-loop-helix TF E protein regulating Rag gene CREs, as well as the evolution of the antagonist of this protein, the Id protein. This may help to understand how the adaptive immune system develops along with the evolution of responsible TFs and enhancers.
Keywords: E protein; Id protein; Rag1/2 gene enhancers; T and B cell development; adaptive immune system; bHLH transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
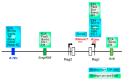

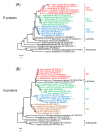
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

