Nanotoxicity of 2D Molybdenum Disulfide, MoS2, Nanosheets on Beneficial Soil Bacteria, Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 34072663
- PMCID: PMC8229097
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11061453
Nanotoxicity of 2D Molybdenum Disulfide, MoS2, Nanosheets on Beneficial Soil Bacteria, Bacillus cereus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
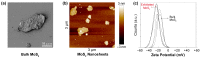
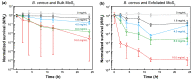
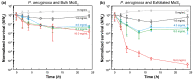
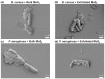
Concerns arising from accidental and occasional releases of novel industrial nanomaterials to the environment and waterbodies are rapidly increasing as the production and utilization levels of nanomaterials increase every day. In particular, two-dimensional nanosheets are one of the most significant emerging classes of nanomaterials used or considered for use in numerous applications and devices. This study deals with the interactions between 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets and beneficial soil bacteria. It was found that the log-reduction in the survival of Gram-positive Bacillus cereus was 2.8 (99.83%) and 4.9 (99.9988%) upon exposure to 16.0 mg/mL bulk MoS2 (macroscale) and 2D MoS2 nanosheets (nanoscale), respectively. For the case of Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa, the log-reduction values in bacterial survival were 1.9 (98.60%) and 5.4 (99.9996%) for the same concentration of bulk MoS2 and MoS2 nanosheets, respectively. Based on these findings, it is important to consider the potential toxicity of MoS2 nanosheets on beneficial soil bacteria responsible for nitrate reduction and nitrogen fixation, soil formation, decomposition of dead and decayed natural materials, and transformation of toxic compounds into nontoxic compounds to adequately assess the environmental impact of 2D nanosheets and nanomaterials.
Keywords: 2D nanosheets; MoS2 nanomaterials; nanotoxicity; soil bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Oh J.K., Liu S., Jones M., Yegin Y., Hao L., Tolen T.N., Nagabandi N., Scholar E.A., Castillo A., Taylor T.M., et al. Modification of aluminum surfaces with superhydrophobic nanotextures for enhanced food safety and hygiene. Food Control. 2019;96:463–469. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.10.005. - DOI
-
- Dimkpa C.O., McLean J.E., Latta D.E., Manangón E., Britt D.W., Johnson W.P., Boyanov M.I., Anderson A.J. CuO and ZnO nanoparticles: Phytotoxicity, metal speciation, and induction of oxidative stress in sand-grown wheat. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012;14:1125. doi: 10.1007/s11051-012-1125-9. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

