Quantification of the Direct Solar Impact on Some Components of the Hydro-Climatic System
- PMID: 34072681
- PMCID: PMC8228176
- DOI: 10.3390/e23060691
Quantification of the Direct Solar Impact on Some Components of the Hydro-Climatic System
Abstract
This study addresses the causal links between external factors and the main hydro-climatic variables by using a chain of methods to unravel the complexity of the direct sun-climate link. There is a gap in the literature on the description of a complete chain in addressing the structures of direct causal links of solar activity on terrestrial variables. This is why the present study uses the extensive facilities of the application of information theory in view of recent advances in different fields. Additionally, by other methods (e.g., neural networks) we first tested the existent non-linear links of solar-terrestrial influences on the hydro-climate system. The results related to the solar impact on terrestrial phenomena are promising, which is discriminant in the space-time domain. The implications prove robust for determining the causal measure of climate variables under direct solar impact, which makes it easier to consider solar activity in climate models by appropriate parametrizations. This study found that hydro-climatic variables are sensitive to solar impact only for certain frequencies (periods) and have a coherence with the Solar Flux only for some lags of the Solar Flux (in advance).
Keywords: causality; climate response; entropy transfer; neural networks; solar impact; time series; wavelet analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
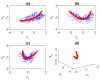
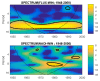
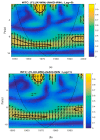

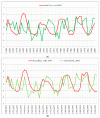
Similar articles
-
Assessing the solar variability signature in climate variables by information theory and wavelet coherence.Sci Rep. 2021 May 31;11(1):11337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90044-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34059693 Free PMC article.
-
Chronoastrobiology: proposal, nine conferences, heliogeomagnetics, transyears, near-weeks, near-decades, phylogenetic and ontogenetic memories.Biomed Pharmacother. 2004 Oct;58 Suppl 1:S150-87. doi: 10.1016/s0753-3322(04)80025-8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2004. PMID: 15754855
-
An Information Theory Approach to Identifying a Representative Subset of Hydro-Climatic Simulations for Impact Modeling Studies.Water Resour Res. 2018 Aug;54(8):5422-5435. doi: 10.1029/2017WR022035. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Water Resour Res. 2018. PMID: 30344354 Free PMC article.
-
Terrestrial ecosystems, increased solar ultraviolet radiation, and interactions with other climate change factors.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2007 Mar;6(3):252-66. doi: 10.1039/b700019g. Epub 2007 Feb 1. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17344961 Review.
-
Global warming 2007. An update to global warming: the balance of evidence and its policy implications.ScientificWorldJournal. 2007 Mar 9;7:381-99. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2007.91. ScientificWorldJournal. 2007. PMID: 17370024 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selection of Optimal Palmer Predictors for Increasing the Predictability of the Danube Discharge: New Findings Based on Information Theory and Partial Wavelet Coherence Analysis.Entropy (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;24(10):1375. doi: 10.3390/e24101375. Entropy (Basel). 2022. PMID: 37420396 Free PMC article.
-
Information Generating Function of Ranked Set Samples.Entropy (Basel). 2021 Oct 21;23(11):1381. doi: 10.3390/e23111381. Entropy (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34828079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saltzman B. Advances in Geophysics. Volume 20. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: San Francisco, CA, USA: London, UK: 1978. A survey of statistical–dynamical models of the terrestrial climate; pp. 183–304.
-
- Wen G., Cahalan R.F., Rind D., Jonas J., Pilewskie P., Dong L., Wu D.L., Krivova N.A. Climate responses to SATIRE and SIM-based spectral solar forcing in a 3D atmosphere-ocean coupled GCM. Published by EDP Sciences. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2017;7:A11. doi: 10.1051/swsc/2017009. - DOI
-
- Zhang G., Su X., Singh V.P., Ayantobo O.O. Modeling NDVI Using Joint Entropy Method Considering Hydro-Meteorological Driving Factors in the Middle Reaches of Hei River Basin. Entropy. 2017;19:502. doi: 10.3390/e19090502. - DOI
-
- Smith R. A Mutual Information Approach to Calculating Nonlinearity. Stat. 2015;4:291–303. doi: 10.1002/sta4.96. - DOI
-
- Goodwell A., Jiang P., Ruddell B., Kumar P. Debates -Does Information Theory provide a new paradigm for Earth science? Identifying causality, interaction, and feedback. WRR. 2020;56 doi: 10.1029/2019WR024940. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

