Serum Metabolite Profiles in Participants of Lung Cancer Screening Study; Comparison of Two Independent Cohorts
- PMID: 34072693
- PMCID: PMC8198431
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112714
Serum Metabolite Profiles in Participants of Lung Cancer Screening Study; Comparison of Two Independent Cohorts
Abstract
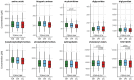
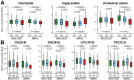
Serum metabolome is a promising source of molecular biomarkers that could support early detection of lung cancer in screening programs based on low-dose computed tomography. Several panels of metabolites that differentiate lung cancer patients and healthy individuals were reported, yet none of them were validated in the population at high-risk of developing cancer. Here we analyzed serum metabolome profiles in participants of two lung cancer screening studies: MOLTEST-BIS (Poland, n = 369) and SMAC-1 (Italy, n = 93). Three groups of screening participants were included: lung cancer patients, individuals with benign pulmonary nodules, and those without any lung alterations. Concentrations of about 400 metabolites (lipids, amino acids, and biogenic amines) were measured by a mass spectrometry-based approach. We observed a reduced level of lipids, in particular cholesteryl esters, in sera of cancer patients from both studies. Despite several specific compounds showing significant differences between cancer patients and healthy controls within each study, only a few cancer-related features were common when both cohorts were compared, which included a reduced concentration of lysophosphatidylcholine LPC (18:0). Moreover, serum metabolome profiles in both noncancer groups were similar, and differences between cancer patients and both groups of healthy participants were comparable. Large heterogeneity in levels of specific metabolites was observed, both within and between cohorts, which markedly impaired the accuracy of classification models: The overall AUC values of three-state classifiers were 0.60 and 0.51 for the test (MOLTEST) and validation (SMAC) cohorts, respectively. Therefore, a hypothetical metabolite-based biomarker for early detection of lung cancer would require adjustment to lifestyle-related confounding factors that putatively affect the composition of serum metabolome.
Keywords: biomarkers; early detection; lung cancer; metabolomics; screening study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- De Koning H.J., Van Der Aalst C.M., De Jong P.A., Scholten E.T., Nackaerts K., Heuvelmans M.A., Lammers J.-W.J., Weenink C., Yousaf-Khan U., Horeweg N., et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with volume CT screening in a randomized trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:503–513. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911793. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wille M.M.W., Dirksen A., Ashraf H., Saghir Z., Bach K.S., Brodersen J., Clementsen P.F., Hansen H.S., Larsen K.R., Mortensen J., et al. Results of the randomized danish lung cancer screening trial with focus on high-risk profiling. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016;193:542–551. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201505-1040OC. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

