Soft Computing of a Medically Important Arthropod Vector with Autoregressive Recurrent and Focused Time Delay Artificial Neural Networks
- PMID: 34072705
- PMCID: PMC8227104
- DOI: 10.3390/insects12060503
Soft Computing of a Medically Important Arthropod Vector with Autoregressive Recurrent and Focused Time Delay Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
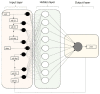
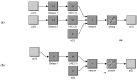
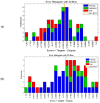
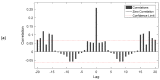
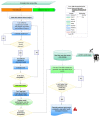
A central issue of public health strategies is the availability of decision tools to be used in the preventive management of the transmission cycle of vector-borne diseases. In this work, we present, for the first time, a soft system computing modeling approach using two dynamic artificial neural network (ANNs) models to describe and predict the non-linear incidence and time evolution of a medically important mosquito species, Culex sp., in Northern Greece. The first model is an exogenous non-linear autoregressive recurrent neural network (NARX), which is designed to take as inputs the temperature as an exogenous variable and mosquito abundance as endogenous variable. The second model is a focused time-delay neural network (FTD), which takes into account only the temperature variable as input to provide forecasts of the mosquito abundance as the target variable. Both models behaved well considering the non-linear nature of the adult mosquito abundance data. Although, the NARX model predicted slightly better (R = 0.623) compared to the FTD model (R = 0.534), the advantage of the FTD over the NARX neural network model is that it can be applied in the case where past values of the population system, here mosquito abundance, are not available for their forecasting.
Keywords: Culex sp.; FTD model; NARX model; decision making; mosquito population system; public health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Design of Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous Model Based Intelligence Computing for Efficient State Estimation of Underwater Passive Target.Entropy (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;23(5):550. doi: 10.3390/e23050550. Entropy (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33947058 Free PMC article.
-
Developing a Mixed Neural Network Approach to Forecast the Residential Electricity Consumption Based on Sensor Recorded Data.Sensors (Basel). 2018 May 5;18(5):1443. doi: 10.3390/s18051443. Sensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29734761 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of spring flows using nonlinear autoregressive exogenous (NARX) neural network models.Environ Monit Assess. 2021 May 22;193(6):350. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09135-6. Environ Monit Assess. 2021. PMID: 34021408
-
Nonlinear autoregressive neural networks with external inputs for forecasting of typhoon inundation level.Environ Monit Assess. 2017 Aug;189(8):376. doi: 10.1007/s10661-017-6100-6. Epub 2017 Jul 5. Environ Monit Assess. 2017. PMID: 28681325
-
Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ANN) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000 Jun;22(5):717-27. doi: 10.1016/s0731-7085(99)00272-1. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2000. PMID: 10815714 Review.
References
-
- WHO Mosquito Borne Diseases. [(accessed on 20 April 2021)];2019 Available online: https://www.who.int/neglected_diseases/vector_ecology/mosquito-borne-dis...
-
- Gratz N.G. The Vector- and Rodent-Borne Diseases of Europe and North America: Their Distribution and Public Health Burden. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2006.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

