Nitrate- and Nitrite-Sensing Histidine Kinases: Function, Structure, and Natural Diversity
- PMID: 34072989
- PMCID: PMC8199190
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115933
Nitrate- and Nitrite-Sensing Histidine Kinases: Function, Structure, and Natural Diversity
Abstract
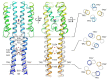
Under anaerobic conditions, bacteria may utilize nitrates and nitrites as electron acceptors. Sensitivity to nitrous compounds is achieved via several mechanisms, some of which rely on sensor histidine kinases (HKs). The best studied nitrate- and nitrite-sensing HKs (NSHKs) are NarQ and NarX from Escherichia coli. Here, we review the function of NSHKs, analyze their natural diversity, and describe the available structural information. In particular, we show that around 6000 different NSHK sequences forming several distinct clusters may now be found in genomic databases, comprising mostly the genes from Beta- and Gammaproteobacteria as well as from Bacteroidetes and Chloroflexi, including those from anaerobic ammonia oxidation (annamox) communities. We show that the architecture of NSHKs is mostly conserved, although proteins from Bacteroidetes lack the HAMP and GAF-like domains yet sometimes have PAS. We reconcile the variation of NSHK sequences with atomistic models and pinpoint the structural elements important for signal transduction from the sensor domain to the catalytic module over the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions spanning more than 200 Å.
Keywords: allostery; cell signaling; histidine kinases; nitrate regulation; nitrate respiration; signal transduction; two-component systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
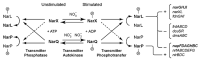








Similar articles
-
Sensor Histidine Kinase NarQ Activates via Helical Rotation, Diagonal Scissoring, and Eventually Piston-Like Shifts.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 28;21(9):3110. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093110. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32354084 Free PMC article.
-
'Locked-on' and 'locked-off' signal transduction mutations in the periplasmic domain of the Escherichia coli NarQ and NarX sensors affect nitrate- and nitrite-dependent regulation by NarL and NarP.Mol Microbiol. 1997 Jun;24(5):1049-60. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4131779.x. Mol Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9220011
-
Signal-dependent phosphorylation of the membrane-bound NarX two-component sensor-transmitter protein of Escherichia coli: nitrate elicits a superior anion ligand response compared to nitrite.J Bacteriol. 1999 Sep;181(17):5309-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.17.5309-5316.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10464202 Free PMC article.
-
Signal Sensing and Transduction by Histidine Kinases as Unveiled through Studies on a Temperature Sensor.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Jun 20;50(6):1359-1366. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00593. Epub 2017 May 5. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28475313 Review.
-
Transmembrane Signal Transduction in Two-Component Systems: Piston, Scissoring, or Helical Rotation?Bioessays. 2018 Feb;40(2). doi: 10.1002/bies.201700197. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 29280502 Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon source, cell density, and the microbial community control inhibition of V. cholerae surface colonization by environmental nitrate.mBio. 2025 Apr 9;16(4):e0406624. doi: 10.1128/mbio.04066-24. Epub 2025 Feb 25. mBio. 2025. PMID: 39998205 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity in Sensing and Signaling of Bacterial Sensor Histidine Kinases.Biomolecules. 2021 Oct 15;11(10):1524. doi: 10.3390/biom11101524. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34680156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alteromonas nitratireducens sp. nov., a Novel Nitrate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Marine Sediments, and the Evolution of Nitrate-Reducing Genes in the Genus Alteromonas.Microorganisms. 2025 Aug 13;13(8):1888. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13081888. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40871392 Free PMC article.
-
From genes to function: regulation, maturation, and evolution of cytochrome c nitrite reductase in nitrate reduction to ammonium.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jul 23;91(7):e0029225. doi: 10.1128/aem.00292-25. Epub 2025 Jun 9. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40488517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Bacterial Communication and Their Biocontrol.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 16;25(10):5443. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105443. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wassenaar T.M., Wanchai V., Alkam D., Nookaew I., Ussery D.W. Conservation of two-component signal transduction systems in E. coli, Salmonella, and Across 100,000 bacteria of various bacterial Phyla. In: Rampelotto P.H., editor. Molecular Mechanisms of Microbial Evolution. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2018. pp. 153–174. Grand Challenges in Biology and, Biotechnology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

