Effects of Reducing L-Carnitine Supplementation on Carnitine Kinetics and Cardiac Function in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 34073024
- PMCID: PMC8230272
- DOI: 10.3390/nu13061900
Effects of Reducing L-Carnitine Supplementation on Carnitine Kinetics and Cardiac Function in Hemodialysis Patients: A Multicenter, Single-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
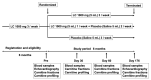
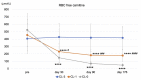
L-carnitine (LC) supplementation improves cardiac function in hemodialysis (HD) patients. However, whether reducing LC supplementation affects carnitine kinetics and cardiac function in HD patients treated with LC remains unclear. Fifty-nine HD patients previously treated with intravenous LC 1000 mg per HD session (three times weekly) were allocated to three groups: LC injection three times weekly, once weekly, and placebo, and prospectively followed up for six months. Carnitine fractions were assessed by enzyme cycling methods. Plasma and red blood cell (RBC) acylcarnitines were profiled using tandem mass spectrometry. Cardiac function was evaluated using echocardiography and plasma B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels. Reducing LC administration to once weekly significantly decreased plasma carnitine fractions and RBC-free carnitine levels during the study period, which were further decreased in the placebo group (p < 0.001). Plasma BNP levels were significantly elevated in the placebo group (p = 0.03). Furthermore, changes in RBC (C16 + C18:1)/C2 acylcarnitine ratio were positively correlated with changes in plasma BNP levels (β = 0.389, p = 0.005). Reducing LC administration for six months significantly decreased both plasma and RBC carnitine levels, while the full termination of LC increased plasma BNP levels; however, it did not influence cardiac function in HD patients.
Keywords: CPT2; acylcarnitine; brain natriuretic peptide; cardiac function; cardiomyopathy; carnitine deficiency; end-stage kidney disease; free fatty acid; heart failure; hemodialysis.
Conflict of interest statement
K.F. has received honoraria, including lecture fees, from Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of hemodialysis session on the dynamics of carnitine ester profile changes in L-carnitine pretreated end-stage renal disease patients.Int Urol Nephrol. 2013 Jun;45(3):847-55. doi: 10.1007/s11255-012-0209-x. Epub 2012 Jun 10. Int Urol Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 22684763
-
Anemia and carnitine supplementation in hemodialyzed patients.Kidney Int Suppl. 1999 Mar;69:S93-106. Kidney Int Suppl. 1999. PMID: 10084293 Clinical Trial.
-
Levocarnitine Improves Cardiac Function in Hemodialysis Patients With Left Ventricular Hypertrophy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Feb;67(2):260-70. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.09.010. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 26508680 Clinical Trial.
-
Carnitine replacement in end-stage renal disease and hemodialysis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Nov;1033:52-66. doi: 10.1196/annals.1320.005. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15591003 Review.
-
L-carnitine in dialysis patients.Semin Dial. 2001 May-Jun;14(3):209-17. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-139x.2001.00055.x. Semin Dial. 2001. PMID: 11422928 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Intravenous Versus Oral Administration of Levocarnitine in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial Investigating Therapeutic Approaches to Renal Anemia.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 5;8(1):e70297. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70297. eCollection 2025 Jan. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39763581 Free PMC article.
-
"Exploring benefits of L-carnitine in hemodialysis: promising findings await clinical application".Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Apr 25. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04550-x. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40281379
-
Development and validation of an UHPLC-Orbitrap-HRMS method for rapid determination of endogenous L-carnitine in patients on hemodialysis/peritoneal dialysis and its application to promote rational drug use.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jan;10(2):103. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-6784. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35282068 Free PMC article.
-
Carnitine supplements for people with chronic kidney disease requiring dialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 6;12(12):CD013601. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013601.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36472884 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of L-carnitine supplementation on lipid profile in adult patients under hemodialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Dec 2;11:1454921. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1454921. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39687901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- House A.A., Wanner C., Sarnak M.J., Piña I.L., McIntyre C.W., Komenda P., Kasiske B.L., Deswal A., de Filippi C.R., Cleland J.G.F., et al. Heart Failure in Chronic Kidney Disease: Conclusions From a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2019;95:1304–1317. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.02.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nitta K., Abe M., Masakane I., Hanafusa N., Taniguchi M., Hasegawa T., Nakai S., Wada A., Hamano T., Hoshino J., et al. Annual dialysis data report 2018, JSDT Renal Data Registry: Dialysis fluid quality, hemodialysis and hemodiafiltration, peritoneal dialysis, and diabetes. Ren. Replace Ther. 2020;6:51. doi: 10.1186/s41100-020-00290-z. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

