Molecular Mechanisms of Antiproliferative Effects of Natural Chalcones
- PMID: 34073042
- PMCID: PMC8198114
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13112730
Molecular Mechanisms of Antiproliferative Effects of Natural Chalcones
Abstract
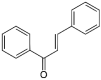
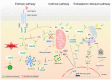
Although great progress has been made in the treatment of cancer, the search for new promising molecules with antitumor activity is still one of the greatest challenges in the fight against cancer due to the increasing number of new cases each year. Chalcones (1,3-diphenyl-2-propen-1-one), the precursors of flavonoid synthesis in higher plants, possess a wide spectrum of biological activities including antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anticancer. A plethora of molecular mechanisms of action have been documented, including induction of apoptosis, autophagy, or other types of cell death, cell cycle changes, and modulation of several signaling pathways associated with cell survival or death. In addition, blockade of several steps of angiogenesis and proteasome inhibition has also been documented. This review summarizes the basic molecular mechanisms related to the antiproliferative effects of chalcones, focusing on research articles from the years January 2015-February 2021.
Keywords: angiogenesis; apoptosis; autophagy; cell cycle arrest; cell death; chalcones; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Anticancer Potential of Natural Chalcones: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;24(12):10354. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210354. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent trends of chalcones potentialities as antiproliferative and antiresistance agents.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(5):592-604. doi: 10.2174/1871520615666150101130800. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25553434 Review.
-
A Review on Mechanisms of Anti Tumor Activity of Chalcones.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;16(2):200-11. doi: 10.2174/1871520615666150518093144. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25980813 Review.
-
Antiangiogenic Effect of Flavonoids and Chalcones: An Update.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 22;19(1):27. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010027. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29271940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Docking Study, Cytotoxicity, Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Induction of Novel Chalcones Incorporating Thiadiazolyl Isoquinoline in Cervical Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(1):70-83. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666191024121116. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31696811
Cited by
-
Natural Chalcones for the Management of Obesity Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 3;24(21):15929. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115929. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acridine-Based Chalcone 1C and ABC Transporters.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 27;26(9):4138. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094138. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362377 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperforin Suppresses Oncogenic Kinases and Induces Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer Cells.In Vivo. 2023 Jan-Feb;37(1):182-189. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13067. In Vivo. 2023. PMID: 36593022 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic Engineering of Microbial Cell Factories for Biosynthesis of Flavonoids: A Review.Molecules. 2021 Jul 27;26(15):4522. doi: 10.3390/molecules26154522. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34361675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anticancer Potential of Natural Chalcones: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 19;24(12):10354. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210354. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373500 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tocchetti C.G., Cadeddu C., di Lisi D., Femmino S., Madonna R., Mele D., Monte I., Novo G., Penna C., Pepe A., et al. From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Management of Antineoplastic Drug-Induced Cardiovascular Toxicity: A Translational Overview. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2019;30:2110–2153. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6930. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santic Z., Pravdic N., Bevanda M., Galic K. The historical use of medicinal plants in traditional and scientific medicine. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017;29(Suppl. 4):787–792. - PubMed
-
- Hallmann-Mikolajczak A. Ebers Papyrus. The book of medical knowledge of the 16th century B.C. Egyptians. Arch. Hist. Filosophy Med. 2004;67:5–14. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

