On the Road to Fight Cancer: The Potential of G-quadruplex Ligands as Novel Therapeutic Agents
- PMID: 34073075
- PMCID: PMC8198608
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115947
On the Road to Fight Cancer: The Potential of G-quadruplex Ligands as Novel Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
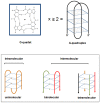
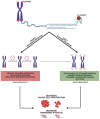
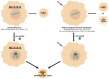
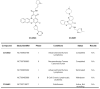
Nucleic acid sequences able to adopt a G-quadruplex conformation are overrepresented within the human genome. This evidence strongly suggests that these genomic regions have been evolutionary selected to play a pivotal role in several aspects of cell biology. In the present review article, we provide an overview on the biological impact of targeting G-quadruplexes in cancer. A variety of small molecules showing good G-quadruplex stabilizing properties has been reported to exert an antitumor activity in several preclinical models of human cancers. Moreover, promiscuous binders and multiple targeting G-quadruplex ligands, cancer cell defense responses and synthetic lethal interactions of G-quadruplex targeting have been also highlighted. Overall, evidence gathered thus far indicates that targeting G-quadruplex may represent an innovative and fascinating therapeutic approach for cancer. The continued methodological improvements, the development of specific tools and a careful consideration of the experimental settings in living systems will be useful to deepen our knowledge of G-quadruplex biology in cancer, to better define their role as therapeutic targets and to help design and develop novel and reliable G-quadruplex-based anticancer strategies.
Keywords: Anticancer therapy; Cancer; Cell defense mechanisms; G-quadruplex; Gene Promoters; Synthetic Lethality; Telomeres.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging Role of G-quadruplex DNA as Target in Anticancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2016;22(44):6612-6624. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666160831101031. Curr Pharm Des. 2016. PMID: 27587203 Review.
-
Tandem application of ligand-based virtual screening and G4-OAS assay to identify novel G-quadruplex-targeting chemotypes.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt B):1341-1352. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.01.024. Epub 2017 Jan 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 28130159
-
Monohydrazone Based G-Quadruplex Selective Ligands Induce DNA Damage and Genome Instability in Human Cancer Cells.J Med Chem. 2020 Mar 26;63(6):3090-3103. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01866. Epub 2020 Mar 18. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32142285 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex structures in the human genome as novel therapeutic targets.Molecules. 2013 Oct 8;18(10):12368-95. doi: 10.3390/molecules181012368. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24108400 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of the first dual G-triplex/G-quadruplex stabilizing compound: a new opportunity in the targeting of G-rich DNA structures?Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 May;1861(5 Pt B):1271-1280. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27836755
Cited by
-
Observing protein dynamics during DNA-lesion bypass by the replisome.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 21;9:968424. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.968424. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36213113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Telomeres and telomerase in Sarcoma disease and therapy.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Aug 6;21(11):2065-2080. doi: 10.7150/ijms.97485. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39239547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-Methyl- and N-Phenylpiperazine Functionalized Styryl Dyes Inside Cucurbiturils: Theoretical Assessment of the Factors Governing the Host-Guest Recognition.Molecules. 2023 Dec 16;28(24):8130. doi: 10.3390/molecules28248130. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38138619 Free PMC article.
-
Carbazole Derivatives Binding to Bcl-2 Promoter Sequence G-quadruplex.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 9;17(7):912. doi: 10.3390/ph17070912. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065762 Free PMC article.
-
Small Heterocyclic Ligands as Anticancer Agents: QSAR with a Model G-Quadruplex.Molecules. 2022 Nov 4;27(21):7577. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217577. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364401 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

