Extracellular Vesicles: Versatile Nanomediators, Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents in Atherosclerosis and COVID-19-Related Thrombosis
- PMID: 34073119
- PMCID: PMC8198837
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115967
Extracellular Vesicles: Versatile Nanomediators, Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Agents in Atherosclerosis and COVID-19-Related Thrombosis
Abstract
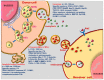
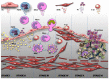
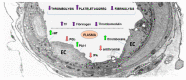
Cells convey information among one another. One instrument employed to transmit data and constituents to specific (target) cells is extracellular vesicles (EVs). They originate from a variety of cells (endothelial, immune cells, platelets, mesenchymal stromal cells, etc.), and consequently, their surface characteristics and cargo vary according to the paternal cell. The cargo could be DNA, mRNA, microRNA, receptors, metabolites, cytoplasmic proteins, or pathological molecules, as a function of which EVs exert different effects upon endocytosis in recipient cells. Recently, EVs have become important participants in a variety of pathologies, including atherogenesis and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated thrombosis. Herein, we summarize recent advances and some of our own results on the role of EVs in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, and discuss their potential to function as signaling mediators, biomarkers and therapeutic agents. Since COVID-19 patients have a high rate of thrombotic events, a special section of the review is dedicated to the mechanism of thrombosis and the possible therapeutic potential of EVs in COVID-19-related thrombosis. Yet, EV mechanisms and their role in the transfer of information between cells in normal and pathological conditions remain to be explored.
Keywords: COVID-19; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular disease; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; microvesicles; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Tokarz A., Szuścik I., Kuśnierz-Cabala B., Kapusta M., Konkolewska M., Żurakowski A., Georgescu A., Stępień E. Extracellular vesicles participate in the transport of cytokines and angiogenic factors in diabetic patients with ocular complications. Folia Med. Cracov. 2015;55:35–48. - PubMed
-
- Georgescu A., Alexandru N., Andrei E., Titorencu I., Dragan E., Tarziu C., Ghiorghe S., Badila E., Bartos D., Popov D. Circulating microparticles and endothelial progenitor cells in atherosclerosis: Pharmacological effects of irbesartan. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012;10:680–691. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04650.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

