The Wall-Associated Receptor-Like Kinase TaWAK7D Is Required for Defense Responses to Rhizoctonia cerealis in Wheat
- PMID: 34073183
- PMCID: PMC8199179
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115629
The Wall-Associated Receptor-Like Kinase TaWAK7D Is Required for Defense Responses to Rhizoctonia cerealis in Wheat
Abstract
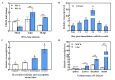
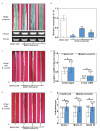
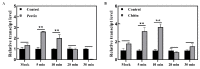
Sharp eyespot, caused by necrotrophic fungus Rhizoctonia cerealis, is a serious fungal disease in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Certain wall-associated receptor kinases (WAK) mediate resistance to diseases caused by biotrophic/hemibiotrophic pathogens in several plant species. Yet, none of wheat WAK genes with positive effect on the innate immune responses to R. cerealis has been reported. In this study, we identified a WAK gene TaWAK7D, located on chromosome 7D, and showed its positive regulatory role in the defense response to R. cerealis infection in wheat. RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analyses showed that TaWAK7D transcript abundance was elevated in wheat after R. cerealis inoculation and the induction in the stem was the highest among the tested organs. Additionally, TaWAK7D transcript levels were significantly elevated by pectin and chitin treatments. The knock-down of TaWAK7D transcript impaired resistance to R. cerealis and repressed the expression of five pathogenesis-related genes in wheat. The green fluorescent protein signal distribution assays indicated that TaWAK7D localized on the plasma membrane in wheat protoplasts. Thus, TaWAK7D, which is induced by R. cerealis, pectin and chitin stimuli, positively participates in defense responses to R. cerealis through modulating the expression of several pathogenesis-related genes in wheat.
Keywords: Rhizoctonia cerealis; defense response; wall-associated receptor kinase; wheat (Triticum aestivum).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The wheat NB-LRR gene TaRCR1 is required for host defence response to the necrotrophic fungal pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis.Plant Biotechnol J. 2017 Jun;15(6):674-687. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12665. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Plant Biotechnol J. 2017. PMID: 27862842 Free PMC article.
-
TaWAK2A-800, a Wall-Associated Kinase, Participates Positively in Resistance to Fusarium Head Blight and Sharp Eyespot in Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 25;22(21):11493. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111493. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768923 Free PMC article.
-
The cysteine-rich receptor-like kinase TaCRK3 contributes to defense against Rhizoctonia cerealis in wheat.J Exp Bot. 2021 Oct 26;72(20):6904-6919. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab328. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 34254642
-
The escalating threat of Rhizoctonia cerealis, the causal agent of sharp eyespot in wheat.Pest Manag Sci. 2011 Nov;67(11):1411-9. doi: 10.1002/ps.2236. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Pest Manag Sci. 2011. PMID: 21726039 Review.
-
Tandem Protein Kinases Emerge as New Regulators of Plant Immunity.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021 Oct;34(10):1094-1102. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-03-21-0073-CR. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2021. PMID: 34096764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wheat Breeding through Genetic and Physical Mapping 2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 12;22(24):13359. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413359. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948157 Free PMC article.
-
An update on evolutionary, structural, and functional studies of receptor-like kinases in plants.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 31;15:1305599. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1305599. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38362444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carbohydrate elicitor-induced plant immunity: Advances and prospects.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 18;10(15):e34871. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34871. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide characterization of the wall-associated kinase-like (WAKL) family in sesame (Sesamum indicum) identifies a SiWAKL6 gene involved in resistance to Macrophomina Phaseolina.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Dec 7;23(1):624. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04658-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 38057720 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Wall-Associated Kinase TaWAK-5D600 Positively Participates in Defense against Sharp Eyespot and Fusarium Crown Rot in Wheat.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 6;24(5):5060. doi: 10.3390/ijms24055060. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science. 2018;361:661. - PubMed
-
- Lemańczyk G., Kwaśna H. Effects of sharp eyespot (Rhizoctonia cerealis) on yield and grain quality of winter wheat. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012:187–200. doi: 10.1007/s10658-012-0077-3. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

