Short Dental Implants (≤8.5 mm) versus Standard Dental Implants (≥10 mm): A One-Year Post-Loading Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 34073250
- PMCID: PMC8199359
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18115683
Short Dental Implants (≤8.5 mm) versus Standard Dental Implants (≥10 mm): A One-Year Post-Loading Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Recent data have shown that short dental implants can be the preferred treatment in most of cases of posterior atrophic alveolar ridges, offering higher survival and lower complication rates than long implants. The survival rates, stability, and marginal bone level changes were compared between short implants (7 and 8.5 mm) and standard-length implants (≥10 mm).
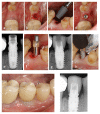
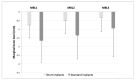
Methods: Prospective observational study in which adult patients requiring ≥1 osseointegrated implants to replace missing teeth were recruited consecutively. A clinical examination was performed on the day the definitive prosthesis was placed and after 6 and 12 months. Implant stability quotient (ISQ), marginal bone level (MBL) changes, and the correlation between these parameters and the characteristics of the implants were evaluated.
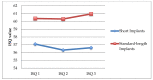
Results: A total of 99 implants were inserted (47 short, 52 standard) in 74 patients. The 12-month survival rate was 100%. ISQ values showed a similar pattern for both types of implants. No correlation was found between ISQ changes after one year and MBL values, nor between the latter and the characteristics of the implants.
Conclusions: With clinical treatment criteria, shorter implants (7 and 8.5 mm in length) can be just as useful as standard-length implants in atrophic alveolar ridges, demonstrating similar rates of survival, stability, and crestal bone loss.
Keywords: dental implants; implant stability; marginal bone level; partial edentulism; short implants; standard implants; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Atieh M., Zadeh H., Stanford C.M., Cooper L.F. Survival of short dental implants for treatment of posterior partial edentulism: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012;27:1323–1331. - PubMed
-
- Buser D., Mericske-Stern R., Bernard J.P.P., Behneke A., Behneke N., Hirt H.P., Belser U.C., Lang N.P. Long-term evaluation of non-submerged ITI implants. Part 1: 8-year life table analysis of a prospective multi-center study with 2359 implants. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1997;8:161–172. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0501.1997.080302.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Telleman G., Raghoebar G.M., Vissink A., den Hartog L., Huddleston Slater J.J.R., Meijer H.J.A. A systematic review of the prognosis of short (<10 mm) dental implants placed in the partially edentulous patient: Systematic review of short dental implants. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011;38:667–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2011.01736.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ravidà A., Barootchi S., Askar H., Del Amo F.S.-L., Tavelli L., Wang H.-L. Long-term effectiveness of extra-short (≤6 mm) dental implants: A systematic review. [(accessed on 4 May 2021)];Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2019 34:68–84. doi: 10.11607/jomi.6893. Available online: http://quintpub.com/journals/omi/abstract.php?iss2_id=1584&article_id=19107. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

