Pullulan Based Bioconjugates for Ocular Dexamethasone Delivery
- PMID: 34073275
- PMCID: PMC8227697
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060791
Pullulan Based Bioconjugates for Ocular Dexamethasone Delivery
Abstract
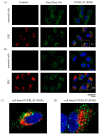
Posterior segment eye diseases are mostly related to retinal pathologies that require pharmacological treatments by invasive intravitreal injections. Reduction of frequent intravitreal administrations may be accomplished with delivery systems that provide sustained drug release. Pullulan-dexamethasone conjugates were developed to achieve prolonged intravitreal drug release. Accordingly, dexamethasone was conjugated to ~67 kDa pullulan through hydrazone bond, which was previously found to be slowly cleavable in the vitreous. Dynamic light scattering and transmission electron microscopy showed that the pullulan-dexamethasone containing 1:20 drug/glucose unit molar ratio (10% w/w dexamethasone) self-assembled into nanoparticles of 461 ± 30 nm and 402 ± 66 nm, respectively. The particles were fairly stable over 6 weeks in physiological buffer at 4, 25 and 37 °C, while in homogenized vitreous at 37 °C, the colloidal assemblies underwent size increase over time. The drug was released slowly in the vitreous and rapidly at pH 5.0 mimicking lysosomal conditions: 50% of the drug was released in about 2 weeks in the vitreous, and in 2 days at pH 5.0. In vitro studies with retinal pigment epithelial cell line (ARPE-19) showed no toxicity of the conjugates in the cells. Flow cytometry and confocal microscopy showed cellular association of the nanoparticles and intracellular endosomal localization. Overall, pullulan conjugates showed interesting features that may enable their successful use in intravitreal drug delivery.
Keywords: controlled release; dexamethasone; hydrazone; ocular drug delivery; pullulan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics of Pullulan-Dexamethasone Conjugates in Retinal Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 21;14(1):12. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010012. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056906 Free PMC article.
-
Screening of chemical linkers for development of pullulan bioconjugates for intravitreal ocular applications.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021 Jun 1;161:105785. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2021.105785. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 33667663
-
Release of functional dexamethasone by intracellular enzymes: A modular peptide-based strategy for ocular drug delivery.J Control Release. 2020 Nov 10;327:584-594. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Sep 8. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32911015
-
Intravitreal Dexamethasone Implant as a Sustained Release Drug Delivery Device for the Treatment of Ocular Diseases: A Comprehensive Review of the Literature.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jul 26;12(8):703. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12080703. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32722556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmaceutical technology can turn a traditional drug, dexamethasone into a first-line ocular medicine. A global perspective and future trends.Int J Pharm. 2017 Jan 10;516(1-2):342-351. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.11.053. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Int J Pharm. 2017. PMID: 27889587 Review.
Cited by
-
Lipid-Based Nanoparticulate Systems for the Ocular Delivery of Bioactives with Anti-Inflammatory Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 11;23(20):12102. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012102. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36292951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology: a comprehensive review for the treatment of eye diseases.Discov Nano. 2025 May 3;20(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s11671-025-04234-6. Discov Nano. 2025. PMID: 40317427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Ocular Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Sep 1;13(9):1383. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13091383. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34575459 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of Pullulan-Dexamethasone Conjugates in Retinal Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Dec 21;14(1):12. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010012. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 35056906 Free PMC article.
-
Zein-Induced Polyelectrolyte Complexes for Encapsulating Triterpenoid Phytochemicals.ACS Omega. 2023 Nov 13;8(47):44637-44646. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05157. eCollection 2023 Nov 28. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38046302 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

