A Dry Powder Platform for Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Dexamethasone: Formulation Development and Nasal Deposition Studies
- PMID: 34073500
- PMCID: PMC8229415
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060795
A Dry Powder Platform for Nose-to-Brain Delivery of Dexamethasone: Formulation Development and Nasal Deposition Studies
Abstract
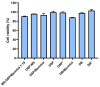
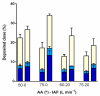
Nasal route of administration offers a unique opportunity of brain targeted drug delivery via olfactory and trigeminal pathway, providing effective CNS concentrations at lower doses and lower risk for adverse reactions compared to systemic drug administration. Therefore, it has been recently proposed as a route of choice for glucocorticoids to control neuroinflammation processes in patients with severe Covid-19. However, appropriate delivery systems tailored to enhance their efficacy yet need to emerge. In this work we present the development of sprayable brain targeting powder delivery platform of dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DSP). DSP-loaded microspheres, optimised employing Quality-by-Design approach, were blended with soluble inert carriers (mannitol or lactose monohydrate). Powder blends were characterized in terms of homogeneity, flow properties, sprayability, in vitro biocompatibility, permeability and mucoadhesion. Nasal deposition studies were performed using 3D printed nasal cavity model. Mannitol provided better powder blend flow properties compared to lactose. Microspheres blended with mannitol retained or enlarged their mucoadhesive properties and enhanced DSP permeability across epithelial model barrier. DSP dose fraction deposited in the olfactory region reached 17.0% revealing the potential of developed powder platform for targeted olfactory delivery. The observed impact of nasal cavity asymmetry highlighted the importance of individual approach when aiming olfactory region.
Keywords: 3D nasal cavity model; dexamethasone sodium phosphate; hypromellose; in vitro nasal deposition; mannitol; nose-to-brain delivery; pectin; spray-dried microspheres.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Drago Špoljarić is from “Visage Technologies d.o.o.”, Vesna Saršon and Maša Safundžić Kučuk are from Jadran-Galenski Laboratorij d.d. Companies Jadran-Galenski Laboratorij d.d. and Visage Technologies d.o.o. had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Cárdenas G., Torres-García D., Cervantes-Torres J., Rosales-Mendoza S., Fleury A., Fragoso G., Laclette J.P., Sciutto E. Role of Systemic and Nasal Glucocorticoid Treatment in the Regulation of the Inflammatory Response in Patients with SARS-Cov-2 Infection. Arch. Med. Res. 2020;52:143–150. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.10.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

