Solubility Determination, Hansen Solubility Parameters and Thermodynamic Evaluation of Thymoquinone in (Isopropanol + Water) Compositions
- PMID: 34073527
- PMCID: PMC8199087
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26113195
Solubility Determination, Hansen Solubility Parameters and Thermodynamic Evaluation of Thymoquinone in (Isopropanol + Water) Compositions
Abstract
This article studies the solubility, Hansen solubility parameters (HSPs), and thermodynamic behavior of a naturally-derived bioactive thymoquinone (TQ) in different binary combinations of isopropanol (IPA) and water (H2O). The mole fraction solubilities (x3) of TQ in various (IPA + H2O) compositions are measured at 298.2-318.2 K and 0.1 MPa. The HSPs of TQ, neat IPA, neat H2O, and binary (IPA + H2O) compositions free of TQ are also determined. The x3 data of TQ are regressed by van't Hoff, Apelblat, Yalkowsky-Roseman, Buchowski-Ksiazczak λh, Jouyban-Acree, and Jouyban-Acree-van't Hoff models. The maximum and minimum x3 values of TQ are recorded in neat IPA (7.63 × 10-2 at 318.2 K) and neat H2O (8.25 × 10-5 at 298.2 K), respectively. The solubility of TQ is recorded as increasing with the rise in temperature and IPA mass fraction in all (IPA + H2O) mixtures, including pure IPA and pure H2O. The HSP of TQ is similar to that of pure IPA, suggesting the great potential of IPA in TQ solubilization. The maximum molecular solute-solvent interactions are found in TQ-IPA compared to TQ-H2O. A thermodynamic study indicates an endothermic and entropy-driven dissolution of TQ in all (IPA + H2O) mixtures, including pure IPA and pure H2O.
Keywords: Hansen solubility parameters; apparent thermodynamics; isopropanol; solubility; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

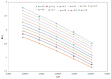
 represents the TQ experimental solubility in (A) neat H2O and (B) neat IPA, and the symbol
represents the TQ experimental solubility in (A) neat H2O and (B) neat IPA, and the symbol  represents the TQ literature solubility values in (A) neat H2O and (B) neat IPA taken from reference [24].
represents the TQ literature solubility values in (A) neat H2O and (B) neat IPA taken from reference [24].
References
-
- Al-Logmani A., Zari T. Long-term effects of Nigella sativa L. oil on some physiological parameters in normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Diab. Mell. 2011;46:46–53. doi: 10.4236/jdm.2011.13007. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

