EFA6 in Axon Regeneration, as a Microtubule Regulator and as a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
- PMID: 34073530
- PMCID: PMC8226579
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10061325
EFA6 in Axon Regeneration, as a Microtubule Regulator and as a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Gonzalez, G.; Chen, L. EFA6 in Axon Regeneration, as a Microtubule Regulator and as a Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor. Cells 2021, 10, 1325.Cells. 2022 May 24;11(11):1721. doi: 10.3390/cells11111721. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35681551 Free PMC article.
Abstract
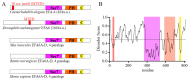
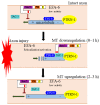
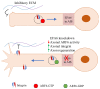
Axon regeneration after injury is a conserved biological process that involves a large number of molecular pathways, including rapid calcium influx at injury sites, retrograde injury signaling, epigenetic transition, transcriptional reprogramming, polarized transport, and cytoskeleton reorganization. Despite the numerous efforts devoted to understanding the underlying cellular and molecular mechanisms of axon regeneration, the search continues for effective target molecules for improving axon regeneration. Although there have been significant historical efforts towards characterizing pro-regenerative factors involved in axon regeneration, the pursuit of intrinsic inhibitors is relatively recent. EFA6 (exchange factor for ARF6) has been demonstrated to inhibit axon regeneration in different organisms. EFA6 inhibition could be a promising therapeutic strategy to promote axon regeneration and functional recovery after axon injury. This review summarizes the inhibitory role on axon regeneration through regulating microtubule dynamics and through affecting ARF6 (ADP-ribosylation factor 6) GTPase-mediated integrin transport.
Keywords: ARF6; EFA6; axon injury; axon regeneration; integrin; microtubule dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

