Prognostic Factors to Predict ICU Mortality in Patients with Severe ARDS Who Received Early and Prolonged Prone Positioning Therapy
- PMID: 34073532
- PMCID: PMC8198972
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10112323
Prognostic Factors to Predict ICU Mortality in Patients with Severe ARDS Who Received Early and Prolonged Prone Positioning Therapy
Abstract
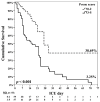
Early and prolonged prone positioning (PP) therapy improve survival in advanced ARDS; however, the predictors of mortality remain unclear. The study aims to identify predictive factors correlated with mortality and build-up the prognostic score in patients with severe ARDS who received early and prolonged PP therapy. A total of 116 patients were enrolled in this retrospective cohort study. Univariate and multivariate regression models were used to estimate the odds ratio (OR) of mortality. Factors associated with mortality were assessed by Cox regression analysis and presented as the hazard ratio (HR) and 95% CI. In the multivariate regression model, renal replacement therapy (RRT; OR: 4.05, 1.54-10.67), malignant comorbidity (OR: 8.86, 2.22-35.41), and non-influenza-related ARDS (OR: 5.17, 1.16-23.16) were significantly associated with ICU mortality. Age, RRT, non-influenza-related ARDS, malignant comorbidity, and APACHE II score were included in a composite prone score, which demonstrated an area under the curve of 0.816 for predicting mortality risk. In multivariable Cox proportional hazard model, prone score more than 3 points was significantly associated with ICU mortality (HR: 2.13, 1.12-4.07, p = 0.021). We suggest prone score ≥3 points could be a good predictor for mortality in severe ARDS received PP therapy.
Keywords: ICU mortality; acute respiratory distress syndrome; prognostic factors; prone positioning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Energy Achievement Rate Is an Independent Factor Associated with Intensive Care Unit Mortality in High-Nutritional-Risk Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Requiring Prolonged Prone Positioning Therapy.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 12;13(9):3176. doi: 10.3390/nu13093176. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579053 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of survival in patients with influenza pneumonia-related severe acute respiratory distress syndrome treated with prone positioning.Ann Intensive Care. 2018 Sep 24;8(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13613-018-0440-4. Ann Intensive Care. 2018. PMID: 30251181 Free PMC article.
-
[Dynamic measurement of volume of atelectasis area in the evaluation of the prognosis of patients with moderate-to-severe acute respiratory distress syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Sep;32(9):1056-1060. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20191219-00056. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33081890 Chinese.
-
Factors Influencing Prone Positioning in Treating Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and the Effect on Mortality Rate.Cureus. 2020 Oct 2;12(10):e10767. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10767. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33033667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prone positioning in acute respiratory distress syndrome.Nurs Stand. 2015 Aug 12;29(50):34-9. doi: 10.7748/ns.29.50.34.e9261. Nurs Stand. 2015. PMID: 26264335 Review.
Cited by
-
Energy Achievement Rate Is an Independent Factor Associated with Intensive Care Unit Mortality in High-Nutritional-Risk Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Requiring Prolonged Prone Positioning Therapy.Nutrients. 2021 Sep 12;13(9):3176. doi: 10.3390/nu13093176. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34579053 Free PMC article.
-
Extended prone positioning for intubated ARDS: a review.Crit Care. 2023 Jul 5;27(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s13054-023-04526-2. Crit Care. 2023. PMID: 37408074 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bellani G., Laffey J.G., Pham T., Fan E., Brochard L., Esteban A., Gattinoni L., Van Haren F., Larsson A., McAuley D.F., et al. Epidemiology, Patterns of Care, and Mortality for Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Intensive Care Units in 50 Countries. JAMA. 2016;315:788–800. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0291. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

