Diabetic Retinopathy Fundus Image Classification and Lesions Localization System Using Deep Learning
- PMID: 34073541
- PMCID: PMC8198489
- DOI: 10.3390/s21113704
Diabetic Retinopathy Fundus Image Classification and Lesions Localization System Using Deep Learning
Abstract
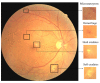
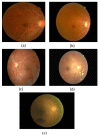
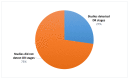
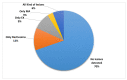
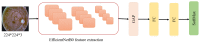
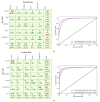
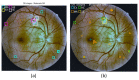
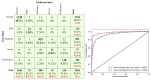
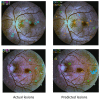
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a disease resulting from diabetes complications, causing non-reversible damage to retina blood vessels. DR is a leading cause of blindness if not detected early. The currently available DR treatments are limited to stopping or delaying the deterioration of sight, highlighting the importance of regular scanning using high-efficiency computer-based systems to diagnose cases early. The current work presented fully automatic diagnosis systems that exceed manual techniques to avoid misdiagnosis, reducing time, effort and cost. The proposed system classifies DR images into five stages-no-DR, mild, moderate, severe and proliferative DR-as well as localizing the affected lesions on retain surface. The system comprises two deep learning-based models. The first model (CNN512) used the whole image as an input to the CNN model to classify it into one of the five DR stages. It achieved an accuracy of 88.6% and 84.1% on the DDR and the APTOS Kaggle 2019 public datasets, respectively, compared to the state-of-the-art results. Simultaneously, the second model used an adopted YOLOv3 model to detect and localize the DR lesions, achieving a 0.216 mAP in lesion localization on the DDR dataset, which improves the current state-of-the-art results. Finally, both of the proposed structures, CNN512 and YOLOv3, were fused to classify DR images and localize DR lesions, obtaining an accuracy of 89% with 89% sensitivity, 97.3 specificity and that exceeds the current state-of-the-art results.
Keywords: YOLO; computer-aided diagnosis; convolutional neural networks; deep learning; diabetic retinopathy; diabetic retinopathy classification; diabetic retinopathy lesions localization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

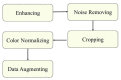
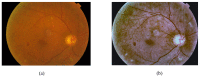
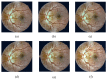
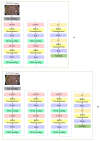

References
-
- American Academy of Ophthalmology-What Is Diabetic Retinopathy. [(accessed on 1 January 2019)]; Available online: https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/what-is-diabetic-retinopathy.
-
- Taylor R., Batey D. Handbook of Retinal Screening in Diabetes: Diagnosis and Management. 2nd ed. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd., Wiley-Blackwell; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2012. pp. 1–173. - DOI
-
- Wilkinson C.P., Ferris F.L., Klein R.E., Lee P.P., Agardh C.D., Davis M., Dills D., Kampik A., Pararajasegaram R., Verdaguer J.T., et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. 2003;110:1677–1682. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00475-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deng L., Yu D. Deep learning: Methods and applications. Found. Trends Signal Process. 2014;7:197–387. doi: 10.1561/2000000039. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

