PPARα Agonist, MHY3200, Alleviates Renal Inflammation during Aging via Regulating ROS/Akt/FoxO1 Signaling
- PMID: 34073584
- PMCID: PMC8198004
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26113197
PPARα Agonist, MHY3200, Alleviates Renal Inflammation during Aging via Regulating ROS/Akt/FoxO1 Signaling
Abstract
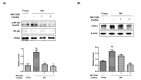
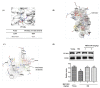
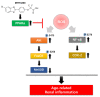
PPARα is a ligand-dependent transcription factor and its activation is known to play an important role in cell defense through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. MHY3200 (2-[4-(5-chlorobenzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)phenoxy]-2,2-difluoroacetic acid), a novel benzothiazole-derived peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) agonist, is a synthesized PPARα activator. This study examined the beneficial effects of MHY3200 on age-associated alterations in reactive oxygen species (ROS)/Akt/forkhead box (FoxO) 1 signaling in rat kidneys. Young (7-month-old) and old (22-month-old) rats were treated with MHY3200 (1 mg/kg body weight/day or 3 mg/kg body weight/day) for two weeks. MHY3200 treatment led to a notable decrease in triglyceride and insulin levels in serum from old rats. The elevated kidney ROS level, serum insulin level, and Akt phosphorylation in old rats were reduced following MHY3200 treatment; moreover, FoxO1 phosphorylation increased. MHY3200 treatment led to the increased level of FoxO1 and its target gene, MnSOD. MHY3200 suppressed cyclooxygenase-2 expression by activating PPARα and inhibiting the activation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) in the kidneys of old rats. Our results suggest that MHY3200 ameliorates age-associated renal inflammation by regulating NF-κB and FoxO1 via ROS/Akt signaling.
Keywords: Akt; MHY3200; NF-κB; ROS; aging; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Knight J.A. The biochemistry of aging. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2000;35:1–62. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

