The Expression of Non-Coding RNAs and Their Target Molecules in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Molecular Basis for Rheumatoid Pathogenesis and Its Potential Clinical Applications
- PMID: 34073629
- PMCID: PMC8198764
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115689
The Expression of Non-Coding RNAs and Their Target Molecules in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Molecular Basis for Rheumatoid Pathogenesis and Its Potential Clinical Applications
Abstract
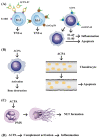
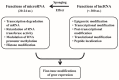
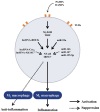
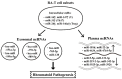
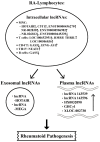
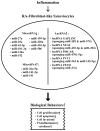
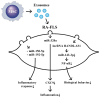
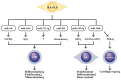
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a typical autoimmune-mediated rheumatic disease presenting as a chronic synovitis in the joint. The chronic synovial inflammation is characterized by hyper-vascularity and extravasation of various immune-related cells to form lymphoid aggregates where an intimate cross-talk among innate and adaptive immune cells takes place. These interactions facilitate production of abundant proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines and growth factors for the proliferation/maturation/differentiation of B lymphocytes to become plasma cells. Finally, the autoantibodies against denatured immunoglobulin G (rheumatoid factors), EB virus nuclear antigens (EBNAs) and citrullinated protein (ACPAs) are produced to trigger the development of RA. Furthermore, it is documented that gene mutations, abnormal epigenetic regulation of peptidylarginine deiminase genes 2 and 4 (PADI2 and PADI4), and thereby the induced autoantibodies against PAD2 and PAD4 are implicated in ACPA production in RA patients. The aberrant expressions of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) including microRNAs (miRs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in the immune system undoubtedly derange the mRNA expressions of cytokines/chemokines/growth factors. In the present review, we will discuss in detail the expression of these ncRNAs and their target molecules participating in developing RA, and the potential biomarkers for the disease, its diagnosis, cardiovascular complications and therapeutic response. Finally, we propose some prospective investigations for unraveling the conundrums of rheumatoid pathogenesis.
Keywords: RANK-RANKL-OPG signaling; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; anti-citrullinated protein antibody; bone-marrow-derived stem cell; fibroblast-like synoviocyte; non-coding RNA; peptidylarginine deiminase; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PAD enzymes in rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic effectors and autoimmune targets.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;16(6):301-315. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0409-1. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32341463 Review.
-
Macrophage extracellular traps require peptidylarginine deiminase 2 and 4 and are a source of citrullinated antigens bound by rheumatoid arthritis autoantibodies.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 27;15:1167362. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1167362. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38476240 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):2069-78. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.002. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23602936 Review.
-
Iguratimod dose dependently inhibits the expression of citrullinated proteins and peptidylarginine deiminases 2 and 4 in neutrophils from rheumatoid arthritis patients.Clin Rheumatol. 2020 Mar;39(3):899-907. doi: 10.1007/s10067-019-04835-4. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Clin Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 31758423
-
Molecular Factors in PAD2 (PADI2) and PAD4 (PADI4) Are Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease Susceptibility in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Cells. 2023 Sep 8;12(18):2235. doi: 10.3390/cells12182235. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37759458 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of Autophagy as a Trigger of Post-Translational Modifications of Proteins and Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 14;24(16):12764. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612764. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating Vitreous microRNA as Possible Biomarker in High Myopic Eyes with Macular Hole.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 26;23(7):3647. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073647. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409006 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miRNAs involvement in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 15;11(2):e41983. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41983. eCollection 2025 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39897907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of lncRNA NEAT1 induces dysfunction of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis via miRNA-338-3p-mediated regulation of glutamine metabolism.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Sep 1;17(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03295-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 36050752 Free PMC article.
-
Demethylase FTO mediates m6A modification of ENST00000619282 to promote apoptosis escape in rheumatoid arthritis and the intervention effect of Xinfeng Capsule.Front Immunol. 2025 Mar 13;16:1556764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1556764. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40181982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angelotti F., Parma A., Cafaro G., Capecchi R., Alunno A., Puxeddu I. One year in review 2017: Pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017;35:368–378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

