Physiological, Morphological and Antioxidant Responses of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6 Isolated from Harbin Dry Sausages to Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 34073637
- PMCID: PMC8229211
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10061203
Physiological, Morphological and Antioxidant Responses of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6 Isolated from Harbin Dry Sausages to Oxidative Stress
Abstract
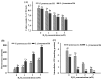
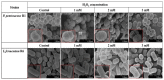
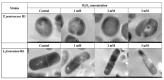
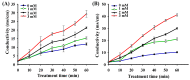
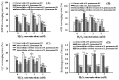
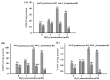
As functional starter cultures and potential probiotics, the ability of lactic acid bacteria to resist oxidative stress is essential to maintain viability and functional properties. This study investigates the effects of H2O2 at different concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 3 mM) on the physiological, morphological, and antioxidant properties of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6 isolated from Harbin dry sausages. The increase in H2O2 concentration induced a significant increase in reactive oxygen species and a decrease in intracellular ATP levels (p < 0.05). Based on scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and electric conductivity analysis, H2O2 stress caused cell deformation, the destruction of cell membrane integrity, partial loss of the cytoplasm, and an increase in the cell conductivity of both strains. H2O2 stress with 1 mM or 2 mM concentrations could effectively improve the scavenging rates of free radicals, the activities of superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxide, and the total antioxidant capacity of both strains (p < 0.05). In conclusion, an appropriate oxidative stress contributed to the activation of the antioxidant defense system of both strains, conferred strains a better effect in inhibiting the oxidation of fermented foods, and improved the health of the host.
Keywords: Lactobacillus fermentum; Pediococcus pentosaceus; antioxidant activity; cell morphology; oxidative stress; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant potential of a unique LAB culture isolated from Harbin dry sausage: In vitro and in a sausage model.Meat Sci. 2015 Dec;110:180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2015.07.021. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Meat Sci. 2015. PMID: 26241464
-
Effect of glycine and Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 combined application on the physicochemical properties, oxidative stability, and taste profile of Harbin dry sausages.Meat Sci. 2024 Nov;217:109614. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2024.109614. Epub 2024 Jul 28. Meat Sci. 2024. PMID: 39089084
-
l-glycine and l-glutamic acid protect Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 against oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide.Food Microbiol. 2022 Feb;101:103897. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2021.103897. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Food Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34579850
-
In vitro growth performance, antioxidant activity and cell surface physiological characteristics of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6 stressed at different NaCl concentrations.Food Funct. 2020 Jul 22;11(7):6376-6386. doi: 10.1039/c9fo02309g. Food Funct. 2020. PMID: 32613220
-
Lactobacillus fermentum JX306 Restrain D-galactose-induced Oxidative Stress of Mice through its Antioxidant Activity.Pol J Microbiol. 2020 Sep;69(2):205-215. doi: 10.33073/pjm-2020-024. Epub 2020 Jun 4. Pol J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32548989 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Ultrasonic Stress on Survival and β-Glucosidase Activity of Encapsulated Lactiplantibacillus plantarum BCRC 10357 in Fermentation of Black Soymilk.Foods. 2022 Apr 25;11(9):1234. doi: 10.3390/foods11091234. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35563956 Free PMC article.
-
Fortified Fermented Rice-Acid Can Regulate the Gut Microbiota in Mice and Improve the Antioxidant Capacity.Nutrients. 2021 Nov 24;13(12):4219. doi: 10.3390/nu13124219. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34959769 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiome Diversity in Seafood Factories via Next-Generation Sequencing for Food Safety Management System (FSMS) Certifications in Malaysia.Foods. 2025 Apr 26;14(9):1517. doi: 10.3390/foods14091517. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361602 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of different drying techniques on rose (Rosa rugosa cv. Plena) proteome based on label-free quantitative proteomics.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 21;9(2):e13158. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13158. eCollection 2023 Feb. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36747566 Free PMC article.
-
The Changes Occurring in Proteins during Processing and Storage of Fermented Meat Products and Their Regulation by Lactic Acid Bacteria.Foods. 2022 Aug 12;11(16):2427. doi: 10.3390/foods11162427. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36010427 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bekhit M., Arabtehrany E., Kahn C.J.F., Cleymand F., Fleutot S., Desobry S., Sanchezgonzalez L. Bioactive films containing alginate-pectin composite microbeads with Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis: Physicochemical characterization and antilisterial activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:574. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020574. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chávarri M., Marañón I., Ares R., Ibáñez F.C., Marzo F., Villarán M.C. Microencapsulation of a probiotic and prebiotic in alginate-chitosan capsules improves survival in simulated gastro-intestinal conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010;142:185–189. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.06.022. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

