Relationship between Retinal Microvasculature, Cardiovascular Risk and Silent Brain Infarction in Hypertensive Patients
- PMID: 34073652
- PMCID: PMC8224683
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11060937
Relationship between Retinal Microvasculature, Cardiovascular Risk and Silent Brain Infarction in Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
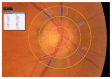
Objective: The aims of this study are to analyze the role of artery-vein ratio AVR assessment using VesselMap 2 software (Imedos Systems) and cardiovascular risk evaluation by means of REGICOR in the prediction of silent brain infarction (SBI) in middle-age hypertensive patients from the ISSYS study.
Material and methods: A cross-sectional study with 695 patients with hypertension aged 50 to 70 years who participated in the project Investigating Silent Strokes in HYpertensives: a Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study (ISSYS), was conducted in two Primary Care Centres of Barcelona. Participants agreed to a retinography and an MRI to detect silent brain infarction (SBI). The IMEDOS software was used for the semiautomatic caliber measurement of retinal arteries and veins, and the AVR was considered abnormal when <0.66. The REGICOR score was calculated for all patients.
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analysis was used to evaluate the impact of AVR and REGICOR scores on SBI. The OR (odds ratio) for a high REGICOR score and an abnormal AVR were 3.16 and 4.45, respectively. When analysing the interaction of both factors, the OR of an abnormal AVR and moderate REGICOR score was 3.27, whereas with a high REGICOR score it reached 13.07.
Conclusions: The measurement of AVR in patients with hypertension and with a high REGICOR score can contribute to the detection of silent brain infarction.
Keywords: cardiovascular risk; hypertension; retinal microvasculature; silent brain infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Longstreth W.T., Jr., Dulberg C., Manolio T.A., Lewis M.R., Beauchamp N.J., Jr., O’Leary D., Carr J., Furberg C.D. Incidence, manifestations, and predictors of brain infarcts defined by serial cranial magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly. Cardiovascular Health Study Stroke. 2002;33:2376–2382. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000032241.58727.49. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bokura H., Kobayashi S., Yamaguchi S., Iijima K., Nagai A., Toyoda G., Oguro H., Takahashi K. Silent brain infarction and subcortical white matter lesions increase the risk of stroke and mortality: A prospective cohort study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2006;15:57–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2005.11.001. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

