Sweet Talk: A Qualitative Study Exploring Attitudes towards Sugar, Sweeteners and Sweet-Tasting Foods in the United Kingdom
- PMID: 34073676
- PMCID: PMC8225159
- DOI: 10.3390/foods10061172
Sweet Talk: A Qualitative Study Exploring Attitudes towards Sugar, Sweeteners and Sweet-Tasting Foods in the United Kingdom
Abstract
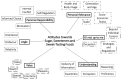
Worldwide initiatives currently aim to reduce free sugar intakes, but success will depend on consumer attitudes towards sugar and the alternatives. This work aimed to explore attitudes towards sugar, sweeteners and sweet-tasting foods, towards consumption and related policies, in a sample of the general public of the UK. Focus groups and interviews were conducted with 34 adults (7 males, ages: 18-65 years). Thematic analysis identified six themes: 'Value' (e.g., pleasure, emotions), 'Angle' (e.g., disinterest), 'Personal Relevance' (to be concerned and/or change one's own behavior), 'Personal Responsibility' (one has an active relationship with these food items), 'Understanding' (the acquisition, comprehension and application of information) and 'It's Not Up to Me' (a passive approach, because intake is subjected to other factors). Both positive and negative attitudes towards sugar, sweeteners and sweet-tasting foods were expressed in all themes. Participants also reported varied engagement with and motivations towards all food items, with implications for intakes. Suggested challenges and potential strategies for reducing free sugar intakes highlighted the need for differing approaches. Future work should assess associations between attitudes and intakes. For greatest population benefit, evidence of the dominant attitudes in those in greatest need of reduced free sugar intakes would be of value.
Keywords: focus groups; perceptions; qualitative research; sweet taste; sweetness; thematic analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Guideline: Sugars Intake for Adults and Children. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. [(accessed on 11 December 2019)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241549028.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical