Factors Influencing Public Attitudes towards COVID-19 Vaccination: A Scoping Review Informed by the Socio-Ecological Model
- PMID: 34073757
- PMCID: PMC8225013
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9060548
Factors Influencing Public Attitudes towards COVID-19 Vaccination: A Scoping Review Informed by the Socio-Ecological Model
Abstract
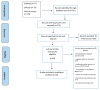
Major hindrances to getting a COVID-19 vaccine include vaccine hesitancy, skepticism, refusal, and anti-vaccine movements. Several studies have been conducted on attitudes of the public towards COVID-19 vaccines and the potential influencing factors. The purpose of this scoping review is to summarize the data available on the various factors influencing public attitudes towards COVID-19 vaccination. This scoping review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) Statement. PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Central were searched without restrictions to reclaim all publications on the factors that shape individuals' attitudes towards COVID-19 vaccines from 1 January 2020 to 15 February 2021. Fifty studies were included. The scoping review revealed that the factors influencing public attitudes towards COVID-19 vaccines were embedded within the different levels of the socio-ecological model. These factors included the sociodemographic characteristics of the individuals, individual factors, social and organizational factors. In addition, certain characteristics of COVID-19 vaccines themselves influenced public attitudes towards accepting the vaccines. Understanding various population needs and the factors shaping public attitudes towards the vaccines would support planning for evidence-based multilevel interventions in order to enhance global vaccine uptake.
Keywords: COVID-19; acceptance; ecological model; hesitancy; refusal; scoping review; vaccine; willingness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Worldometer COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. [(accessed on 21 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/?utm_campaign=homeAdvegas1?
-
- Phua J., Weng L., Ling L., Egi M., Lim C.-M., Divatia J.V., Shrestha B.R., Arabi Y.M., Ng J., Gomersall C.D., et al. Intensive care management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Challenges and recommendations. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020;8:506–517. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30161-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Modes of Transmission of Virus Causing COVID-19: Implications for IPC Precaution Recommendations. [(accessed on 21 March 2021)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/modes-of-transmission-....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources