Mechanical Performance of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Modified with Waste Frying Oil and Crumb Rubber
- PMID: 34073812
- PMCID: PMC8197228
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14112781
Mechanical Performance of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Modified with Waste Frying Oil and Crumb Rubber
Abstract
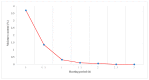
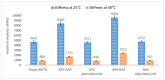
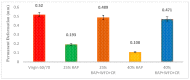
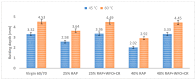
Researchers are exploring the utilisation of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) as a recycled material to determine the performance of non-renewable natural aggregates and other road products such as asphalt binder, in the construction and rehabilitation stage of asphalt pavements. The addition of RAP in asphalt mixtures is a complex process and there is a need to understand the design of the asphalt mixture. Some of the problems associated with adding RAP to asphalt mixtures are moisture damage and cracking damage caused by poor adhesion between the aggregates and asphalt binder. There is a need to add rejuvenators to the recycled mixture containing RAP to enhance its performance, excepting the rutting resistance. This study sought to improve asphalt mixture performance and mechanism by adding waste frying oil (WFO) and crumb rubber (CR) to 25 and 40% of the RAP content. Moreover, the utilisation of CR and WFO improved pavement sustainability and rutting performance. In addition, this study prepared five asphalt mixture samples and compared their stiffness, moisture damage and rutting resistance with the virgin asphalt. The results showed enhanced stiffness and rutting resistance of the RAP but lower moisture resistance. The addition of WFO and CR restored the RAP properties and produced rutting resistance, moisture damage and stiffness, which were comparable to the virgin asphalt mixture. All waste and virgin materials produce homogeneous asphalt mixtures, which influence the asphalt mixture performance. The addition of a high amount of WFO and a small amount of CR enhanced pavement sustainability and rutting performance.
Keywords: RAP; crumb rubber; mechanical performance; moisture damage; recycling; rejuvenator; rutting resistance; waste frying oil.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Li X., Marasteanu M.O., Williams R.C., Clyne T.R. Effect of reclaimed asphalt pavement (proportion and type) and binder grade on asphalt mixtures. Transp. Res. Rec. 2008;2051:90–97. doi: 10.3141/2051-11. - DOI
-
- Cao X., Wang H., Cao X., Sun W., Zhu H., Tang B. Investigation of rheological and chemical properties asphalt binder rejuvenated with waste vegetable oil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018;180:455–463. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.06.001. - DOI
-
- Milad A., Taib A.M., Ahmeda A.G.F., Solla M., Yusoff N.I.M. A review of the use of reclaimed asphalt pavement for road paving applications. J. Teknol. 2020;82:3.
-
- Al-Qadi I., Ozer H., Lambros J., Lippert D., El Khatib A., Khan T., Singh P., Rivera-Perez J.J., Doll B. Testing Protocols to Ensure Mix Performance of High. Asphalt Binder Replacement Mixes Using RAP and RAS. Illinois Center for Transportation; Rantoul, IL, USA: 2015.
-
- Zhao S., Huang B., Shu X., Jia X., Woods M. Laboratory performance evaluation of warm-mix asphalt containing high percentages of reclaimed asphalt pavement. Transp. Res. Rec. 2012;2294:98–105. doi: 10.3141/2294-11. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

