Simulating Peptide Monolayer Formation: GnRH-I on Silica
- PMID: 34073815
- PMCID: PMC8197186
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115523
Simulating Peptide Monolayer Formation: GnRH-I on Silica
Abstract
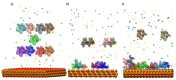
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations can provide a detailed view of molecule behaviour at an atomic level, which can be useful when attempting to interpret experiments or design new systems. The decapeptide gonadotrophin-releasing hormone I (GnRH-I) is known to control fertility in mammals for both sexes. It was previously shown that inoculation with silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) coated with GnRH-I makes an effective anti-fertility vaccine due to how the peptide adsorbs to the nanoparticle and is presented to the immune system. In this paper, we develop and employ a protocol to simulate the development of a GnRH-I peptide adlayer by allowing peptides to diffuse and adsorb in a staged series of trajectories. The peptides start the simulation in an immobile state in solution above the model silica surface, and are then released sequentially. This facile approach allows the adlayer to develop in a natural manner and appears to be quite versatile. We find that the GnRH-I adlayer tends to be sparse, with electrostatics dominating the interactions. The peptides are collapsed to the surface and are seemingly free to interact with additional solutes, supporting the interpretations of the GNRH-I/SiNP vaccine system.
Keywords: GnRH-I; adsorption; molecular dynamics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
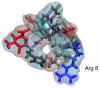

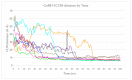
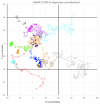
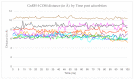
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

