Protein Kinase C as a Therapeutic Target in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 34073823
- PMCID: PMC8197251
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115527
Protein Kinase C as a Therapeutic Target in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
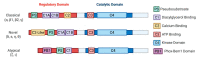
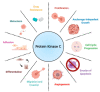
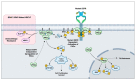
Driver-directed therapeutics have revolutionized cancer treatment, presenting similar or better efficacy compared to traditional chemotherapy and substantially improving quality of life. Despite significant advances, targeted therapy is greatly limited by resistance acquisition, which emerges in nearly all patients receiving treatment. As a result, identifying the molecular modulators of resistance is of great interest. Recent work has implicated protein kinase C (PKC) isozymes as mediators of drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Importantly, previous findings on PKC have implicated this family of enzymes in both tumor-promotive and tumor-suppressive biology in various tissues. Here, we review the biological role of PKC isozymes in NSCLC through extensive analysis of cell-line-based studies to better understand the rationale for PKC inhibition. PKC isoforms α, ε, η, ι, ζ upregulation has been reported in lung cancer, and overexpression correlates with worse prognosis in NSCLC patients. Most importantly, PKC isozymes have been established as mediators of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in NSCLC. Unfortunately, however, PKC-directed therapeutics have yielded unsatisfactory results, likely due to a lack of specific evaluation for PKC. To achieve satisfactory results in clinical trials, predictive biomarkers of PKC activity must be established and screened for prior to patient enrollment. Furthermore, tandem inhibition of PKC and molecular drivers may be a potential therapeutic strategy to prevent the emergence of resistance in NSCLC.
Keywords: chemotherapy; drug resistance; enzastaurin; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); protein kinase C (PKC); targeted therapy; tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ELF3 Is a Target That Promotes Therapeutic Efficiency in EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via Inhibiting PKCί.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 13;22(22):12287. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212287. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830169 Free PMC article.
-
Current Approaches in NSCLC Targeting K-RAS and EGFR.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 14;20(22):5701. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225701. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31739412 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trametinib overcomes KRAS-G12V-induced osimertinib resistance in a leptomeningeal carcinomatosis model of EGFR-mutant lung cancer.Cancer Sci. 2021 Sep;112(9):3784-3795. doi: 10.1111/cas.15035. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 34145930 Free PMC article.
-
MERTK Promotes Resistance to Irreversible EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Non-small Cell Lung Cancers Expressing Wild-type EGFR Family Members.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Dec 15;24(24):6523-6535. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0040. Epub 2018 Sep 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30194074
-
Management of acquired resistance to EGFR TKI-targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0777-1. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling dynamics in coexisting monoclonal cell subpopulations unveil mechanisms of resistance to anti-cancer compounds.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 26;22(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01742-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39061010 Free PMC article.
-
Overcoming cold tumors: a combination strategy of immune checkpoint inhibitors.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 13;15:1344272. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1344272. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38545114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Update on Protein Kinases as Therapeutic Targets-Part I: Protein Kinase C Activation and Its Role in Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 18;24(24):17600. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417600. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LPIN1 Induces Gefitinib Resistance in EGFR Inhibitor-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Apr 29;14(9):2222. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092222. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565351 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor microenvironment signaling and therapeutics in cancer progression.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023 May;43(5):525-561. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12416. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37005490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

