Ceftolozane/Tazobactam for Resistant Drugs Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Infections: A Systematic Literature Review of the Real-World Evidence
- PMID: 34073847
- PMCID: PMC8225018
- DOI: 10.3390/life11060474
Ceftolozane/Tazobactam for Resistant Drugs Pseudomonas aeruginosa Respiratory Infections: A Systematic Literature Review of the Real-World Evidence
Abstract
Background: Ceftolozane/tazobactam (C/T) is a β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor combination that mainly targets Gram-negative bacteria. The current international guidelines recommend including C/T treatment in the empirical therapy for hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) and ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP). Pseudomonas aeruginosa (PA) is one of the most challenging Gram-negative bacteria. We conducted a systematic review of all cases reported in the literature to summarize the existing evidence.
Methods: The main electronic databases were screened to identify case reports of patients with drug-resistant PA respiratory infections treated with C/T.
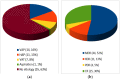
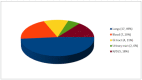
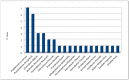
Results: A total of 22 publications were included for a total of 84 infective episodes. The clinical success rate was 72.6% across a wide range of comorbidities. The 45.8% of patients treated with C/T presented colonization by PA. C/T was well tolerated. Only six patients presented adverse events, but none had to stop treatment. The most common therapeutic regimens were 1.5 g every 8 h and 3 g every 8 h.
Conclusion: C/T may be a valid therapeutic option to treat multidrug-resistant (MDR), extensively drug-resistant (XDR), pandrug-resistant (PDR), and carbapenem-resistant (CR) PA infections. However, further data are necessary to define the optimal treatment dosage and duration.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; carbapenem-resistant (CR); ceftolozane/tazobactam; extensively drug-resistant (XDR); hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP); multidrug-resistant (MDR); pandrug-resistant (PDR); ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Zerbaxa (ceftolozane/tazobactam) Letter of Approval. [(accessed on 11 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/014/206829Orig1s000Ap....
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) Zerbaxa (ceftolozane/tazobactam) Letter of Approval. [(accessed on 11 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/zerbaxa#authorisation-....
-
- Solomkin J., Hershberger E., Miller B., Popejoy M., Friedland I., Steenbergen J., Yoon M., Collins S., Yuan G., Barie P.S., et al. Ceftolozane/Tazobactam Plus Metronidazole for Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections in an Era of Multidrug Resistance: Results From a Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase 3 Trial (ASPECT-cIAI) Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015;60:1462–1471. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ097. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wagenlehner F.M., Umeh O., Steenbergen J., Yuan G., Darouiche R.O. Ceftolozane-tazobactam compared with levofloxacin in the treatment of complicated urinary-tract infections, including pyelonephritis: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial (ASPECT-cUTI) Lancet. 2015;385:1949–1956. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62220-0. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources