Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with chronic kidney disease in Spain
- PMID: 34074269
- PMCID: PMC8167969
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-021-06566-2
Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with chronic kidney disease in Spain
Abstract
Background: Data about the impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on health care costs in Spain are scarce This study was aimed to evaluate cumulative costs and healthcare utilisation in CKD in Spain.
Methods: Observational, retrospective, population-based study, which included adults who received care for CKD between 2015 and 2019. Healthcare and medication costs were summarized on a yearly basis starting from the index date (1st January 2015), and then cumulatively until 2019.
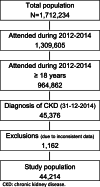
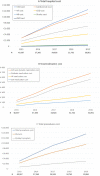
Results: We identified 44,214 patients with CKD (year 2015: age 76.4 ± 14.3 years, 49.0% women, albumin-to-creatinine ratio 362.9 ± 176.8 mg/g, estimated glomerular filtration rate 48.7 ± 13.2 mL/min/1.73 m2). During the 2015-2019 period, cumulative CKD associated costs reached 14,728.4 Euros, being cardiovascular disease hospitalizations, particularly due to heart failure and CKD, responsible for 77.1% of costs. Total medication cost accounted for 6.6% of the total cost. There was a progressive decrease in cardiovascular disease hospital costs per year (from 2741.1 Euros in 2015 to 1.971.7 Euros in 2019). This also occurred with cardiovascular and diabetic medication costs, as well as with the proportion of hospitalizations and mortality. Costs and healthcare resources use were higher in the DAPA-CKD like population, but also decreased over time.
Conclusions: Between 2015 and 2019, costs of patients with CKD in Spain were high, with cardiovascular hospitalizations as the key determinant. Medication costs were responsible for only a small proportion of total CKD costs. Improving CKD management, particularly with the use of cardiovascular and renal protective medications may be helpful to reduce CKD burden.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Cost; DAPA-CKD; Healthcare; Hospitalization; Medication.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Costs and healthcare utilisation of patients with heart failure in Spain.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Oct 20;20(1):964. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05828-9. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 33081776 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, clinical profile, management, and two-year risk complications among patients with chronic kidney disease in Spain.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2021 Nov-Dec;41(6):670-688. doi: 10.1016/j.nefroe.2022.01.008. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2021. PMID: 36165157
-
Clinical Outcomes and Healthcare Resource Utilization in a Real-World Population Reflecting the DAPA-CKD Trial Participants.Adv Ther. 2021 Feb;38(2):1352-1363. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01609-2. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 33474707 Free PMC article.
-
Translating the efficacy of dapagliflozin in chronic kidney disease to lower healthcare resource utilization and costs: a medical care cost offset analysis.J Med Econ. 2023 Jan-Dec;26(1):1407-1416. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2023.2264715. Epub 2023 Oct 31. J Med Econ. 2023. PMID: 37807895 Review.
-
Costs and healthcare use of patients with chronic kidney disease in the Northern Territory, Australia.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Jul 9;24(1):791. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11258-8. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38982437 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Healthcare costs in relation to kidney function among older people: the SCOPE study.Eur Geriatr Med. 2025 Feb;16(1):135-148. doi: 10.1007/s41999-024-01086-8. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Eur Geriatr Med. 2025. PMID: 39535723 Free PMC article.
-
The Economic Impact of Obesity in Turkey: A Micro-Costing Analysis.Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2024 Mar 5;16:123-132. doi: 10.2147/CEOR.S446560. eCollection 2024. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res. 2024. PMID: 38476579 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of outcomes in a Spanish population with chronic kidney disease.Clin Kidney J. 2022 Mar 5;15(7):1415-1424. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac066. eCollection 2022 Jul. Clin Kidney J. 2022. PMID: 35756747 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Obesity in Saudi Arabia: Healthcare Resource Use and Costs Associated with Obesity-Related Complications.Adv Ther. 2023 Apr;40(4):1430-1443. doi: 10.1007/s12325-023-02426-z. Epub 2023 Jan 21. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 36680731 Free PMC article.
-
The economic burden of obesity in 4 south-eastern European countries associated with obesity-related co-morbidities.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Mar 19;24(1):354. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-10840-4. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 38504302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Darlington O, Dickerson C, Evans M, McEwan P, Sörstadius E, Sugrue D, van Haalen H, Garcia Sanchez JJ. Costs and healthcare resource use associated with risk of cardiovascular morbidity in patients with chronic kidney Disease: evidence from a systematic literature review. Adv Ther. 2021;38(2):994–1010. doi: 10.1007/s12325-020-01607-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

