Clusterin serum levels are elevated in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and predict disease activity and treatment response
- PMID: 34075162
- PMCID: PMC8169772
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-90973-2
Clusterin serum levels are elevated in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis and predict disease activity and treatment response
Abstract
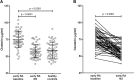
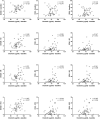
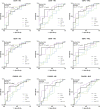
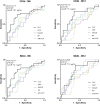
Clusterin (CLU) is a molecular chaperone that participates in a variety of biological processes. Recent studies indicate its possible involvement in the development of bone erosions and autoimmunity. The aim of this study was to investigate its serum concentrations in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and to explore their potential relationship with disease activity and treatment response. Serum levels of CLU were measured in 52 patients before and 3 months after the initiation of treatment and in 52 healthy individuals. CLU levels at baseline were significantly increased in patients with early RA compared with healthy subjects (p < 0.0001). After 3 months of treatment, the levels of CLU decreased and reached concentrations comparable to those in controls. Even though there was no relationship between CLU levels and disease activity at baseline, CLU levels positively correlated with disease activity at months 3, 6 and 12 after treatment initiation. Using ROC analysis, lower CLU baseline levels predicted achieving the therapeutic target of low disease activity and remission at months 3, 6 and 12. In summary, we found increased serum concentrations of clusterin in treatment-naïve patients with early rheumatoid arthritis, and we suggest clusterin as a predictive biomarker of disease activity and treatment response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycosylation Pattern of Serum Clusterin in Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-The Search for New Diagnostic Glycomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 5;25(23):13060. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313060. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684771 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary assessment of serum clusterin as a potential biomarker for canine lymphoma.Vet Comp Oncol. 2020 Sep;18(3):292-302. doi: 10.1111/vco.12550. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Vet Comp Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31654603
-
Exploring the translational potential of clusterin as a biomarker of early osteoarthritis.J Orthop Translat. 2021 Dec 10;32:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2021.10.001. eCollection 2022 Jan. J Orthop Translat. 2021. PMID: 34976733 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduction in serum clusterin is a potential therapeutic biomarker in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer treated with custirsen.Cancer Med. 2013 Aug;2(4):468-77. doi: 10.1002/cam4.93. Epub 2013 May 28. Cancer Med. 2013. PMID: 24156019 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chapter 8: Clusterin: A multifacet protein at the crossroad of inflammation and autoimmunity.Adv Cancer Res. 2009;104:139-70. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(09)04008-1. Adv Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19878776 Review.
Cited by
-
Glycosylation Pattern of Serum Clusterin in Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis-The Search for New Diagnostic Glycomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 5;25(23):13060. doi: 10.3390/ijms252313060. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684771 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of clusterin against interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation in human knee osteoarthritis chondrocytes.Clin Transl Sci. 2024 Jul;17(7):e13881. doi: 10.1111/cts.13881. Clin Transl Sci. 2024. PMID: 38982592 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted immune dysregulation characterizes individuals at-risk for rheumatoid arthritis.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 22;14(1):7637. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43091-8. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37993439 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic and prognostic role of clusterin in diverse musculoskeletal diseases: a mini review.Physiol Res. 2022 Dec 16;71(6):739-747. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934908. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Physiol Res. 2022. PMID: 36281729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysregulation of extracellular vesicle protein cargo in female myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome cases and sedentary controls in response to maximal exercise.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Jan;13(1):e12403. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12403. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38173127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017;76:960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

