A MT-TL1 variant identified by whole exome sequencing in an individual with intellectual disability, epilepsy, and spastic tetraparesis
- PMID: 34075211
- PMCID: PMC8440635
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-021-00900-2
A MT-TL1 variant identified by whole exome sequencing in an individual with intellectual disability, epilepsy, and spastic tetraparesis
Erratum in
-
Correction: A MT-TL1 variant identified by whole exome sequencing in an individual with intellectual disability, epilepsy, and spastic tetraparesis.Eur J Hum Genet. 2021 Sep;29(9):1470-1471. doi: 10.1038/s41431-021-00937-3. Eur J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 34267341 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
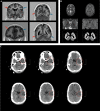
The genetic etiology of intellectual disability remains elusive in almost half of all affected individuals. Within the Solve-RD consortium, systematic re-analysis of whole exome sequencing (WES) data from unresolved cases with (syndromic) intellectual disability (n = 1,472 probands) was performed. This re-analysis included variant calling of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variants, although mtDNA is not specifically targeted in WES. We identified a functionally relevant mtDNA variant in MT-TL1 (NC_012920.1:m.3291T > C; NC_012920.1:n.62T > C), at a heteroplasmy level of 22% in whole blood, in a 23-year-old male with severe intellectual disability, epilepsy, episodic headaches with emesis, spastic tetraparesis, brain abnormalities, and feeding difficulties. Targeted validation in blood and urine supported pathogenicity, with heteroplasmy levels of 23% and 58% in index, and 4% and 17% in mother, respectively. Interestingly, not all phenotypic features observed in the index have been previously linked to this MT-TL1 variant, suggesting either broadening of the m.3291T > C-associated phenotype, or presence of a co-occurring disorder. Hence, our case highlights the importance of underappreciated mtDNA variants identifiable from WES data, especially for cases with atypical mitochondrial phenotypes and their relatives in the maternal line.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Srivastava S, Love-Nichols JA, Dies KA, Ledbetter DH, Martin CL, Chung WK, et al. Meta-analysis and multidisciplinary consensus statement: exome sequencing is a first-tier clinical diagnostic test for individuals with neurodevelopmental disorders. Genet Med. 2019;21:2413–21.. doi: 10.1038/s41436-019-0554-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

