Simeprevir Potently Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Synergizes with Remdesivir
- PMID: 34075346
- PMCID: PMC8056950
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c01186
Simeprevir Potently Suppresses SARS-CoV-2 Replication and Synergizes with Remdesivir
Abstract
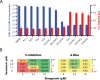
The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is a global threat to human health. Using a multidisciplinary approach, we identified and validated the hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitor simeprevir as an especially promising repurposable drug for treating COVID-19. Simeprevir potently reduces SARS-CoV-2 viral load by multiple orders of magnitude and synergizes with remdesivir in vitro. Mechanistically, we showed that simeprevir not only inhibits the main protease (Mpro) and unexpectedly the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) but also modulates host immune responses. Our results thus reveal the possible anti-SARS-CoV-2 mechanism of simeprevir and highlight the translational potential of optimizing simeprevir as a therapeutic agent for managing COVID-19 and future outbreaks of CoV.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): CUHK and HKU have filed a US provisional patent application based on the finding of this manuscript. W.L.N., M.C.W.C., K.P.Y.H., H.S.L., K.S.K., H.K., and H.-M.L. are inventors of the patent. F.K.L.C. has served as a consultant to Eisai, Pfizer, Takeda, and Otsuka and has been paid lecture fees by Eisai, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Takeda.
Figures



References
-
- Weekly Epidemiological Update–2 February 2021; World Health Organization, 2021.
-
- Chen N.; Zhou M.; Dong X.; Qu J.; Gong F.; Han Y.; Qiu Y.; Wang J.; Liu Y.; Wei Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet 2020, 395 (10223), 507–513. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhou F.; Yu T.; Du R.; Fan G.; Liu Y.; Liu Z.; Xiang J.; Wang Y.; Song B.; Gu X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395 (10229), 1054–1062. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

