Chest X-ray Classification Using Deep Learning for Automated COVID-19 Screening
- PMID: 34075355
- PMCID: PMC8152712
- DOI: 10.1007/s42979-021-00695-5
Chest X-ray Classification Using Deep Learning for Automated COVID-19 Screening
Abstract
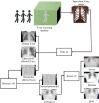
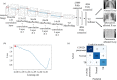
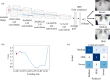
In today's world, we find ourselves struggling to fight one of the worst pandemics in the history of humanity known as COVID-2019 caused by a coronavirus. When the virus reaches the lungs, we observe ground-glass opacity in the chest X-ray due to fibrosis in the lungs. Due to the significant differences between X-ray images of an infected and non-infected person, artificial intelligence techniques can be used to identify the presence and severity of the infection. We propose a classification model that can analyze the chest X-rays and help in the accurate diagnosis of COVID-19. Our methodology classifies the chest X-rays into four classes viz. normal, pneumonia, tuberculosis (TB), and COVID-19. Further, the X-rays indicating COVID-19 are classified on a severity-basis into mild, medium, and severe. The deep learning model used for the classification of pneumonia, TB, and normal is VGG-16 with a test accuracy of 95.9 %. For the segregation of normal pneumonia and COVID-19, the DenseNet-161 was used with a test accuracy of 98.9 %, whereas the ResNet-18 worked best for severity classification achieving a test accuracy up to 76 %. Our approach allows mass screening of the people using X-rays as a primary validation for COVID-19.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s42979-021-00695-5.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chest X-ray; Severity-based classification.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestAuthors A. Shelke, M. Inamdar, V. Shah, A. Tiwari, A. Hussain, T. Chafekar and N. Mehendale declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- King DE. Dlib-ml: A machine learning toolkit. J Mach Learn Res. 2009 Dec 1;10:1755–8.
-
- Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A, Bengio Y. Deep learning, vol. 1. Cambridge: MIT Press; 2016.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
